Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a spherical mirror breaks, what type of mirrors are the individual pieces?
Solution
After the breakdown of the spherical mirror, each piece of the mirror is the same type of original mirror (concave/convex), as the reflective background and curvature have no differences in radius.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
The letter F is placed in front of a plane mirror:
What is the name of the phenomenon involved?
State the kind of mirror used
(a) by a dentist, and
(b) as a street light reflector.
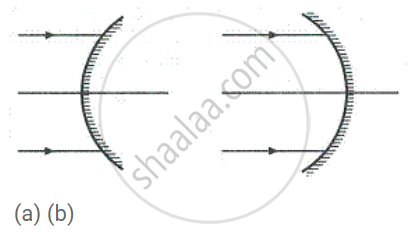
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
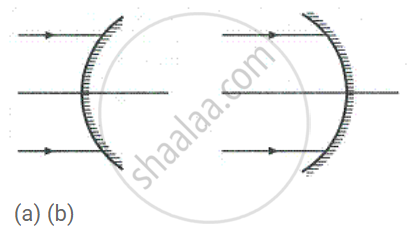
In each case (a) and (b), draw reflected rays for the given incident rays and mark focus by the symbol F.
Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a concave mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
A real and enlarged image can be obtained by using a
An object of height 2 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 12 cm. Find the position, size, and nature of the image.
The sun is seen before the sunrise and after the sunset.
An object forms a virtual image which is 1/8th of the size of the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the convex mirror, calculate:
- the position of the image
- the focal length of the convex mirror.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
Size of image of an object by a mirror having a focal length of 20 cm is observed to be reduced to 1/3rd of its size. At what distance the object has been placed from the mirror? What is the nature of the image and the mirror?
The minimum length of the mirror required to see the full image of the person is half ‘ of his height.
Define the following terms in the context of a diverging mirror:
- Principal focus
- Focal length
Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
