Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the following terms in the context of a diverging mirror:
- Principal focus
- Focal length
Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
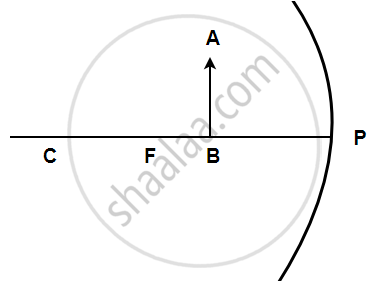
Solution
- Principal focus: The principal focus of the diverging mirror is the point on the principal axis from which all incident rays appear to diverge from behind the mirror.
- Focal length: The distance between the pole and the principal focus of a spherical mirror is called the focal length.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Pole
What do you understand by the focus and focal length of a spherical mirror? Show them on the separate diagrams for each of a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
Explain the following term:
Incident ray
Draw diagram/diagrams to show them.
The diagram below in Figure, shows a convex mirror. C is its centre of curvature and F is its focus. (i) Draw two rays from A and hence locate the position of image of object OA. Label the image IB. (ii) State three characteristics of the image.
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object kept in front of a convex mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
In the following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F) and centre of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
Assertion: Incident ray is directed towards the centre of curvature of spherical mirror. After reflection it retraces its path.
Reason: Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r) = 0°
