Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does the velocity of a stone thrown vertically upwards decreases?
Solution
Velocity of a stone thrown vertically upwards decrease because acceleration due to gravity is acting on downward direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the value of g suddenly becomes twice its value, it will become two times more difficult to pull a heavy object along the floor. Why?
Explain why the value of g is zero at the centre of the earth.
The radius of planet A is half the radius of planet B. If the mass of A is MA, what must be the mass of B so that the value of g on B is half that of its value on A?
The value of gravitational acceleration (g) is ________ at the equator.
Write scientific reason.
The weight of an object varies on different planets.
The ratio of masses of two planets is 2:3 and the ratio of their radii is 4:7 Find the ratio of their accelerations due to gravity.
The acceleration due to gravity on moon is `(1/6)^"th"` times the acceleration due to gravity on earth. If the ratio of the density of earth 'ρe' to the density of moon 'ρm' is `5/3`, then the radius of moon 'Rm' in terms of the radius of earth 'Re' is ______.
At a height R above the earth's surface, the gravitational acceleration is ______.
(R = radius of earth, g = acceleration due to gravity on earth's surface.)
A wire AB is carrying steady current 'I1' and is kept on the table. Another wire CD carrying current 'I2' is held parallel and directly above AB at a distance 'r'. When wire CD is left free and it remains suspended at its position, its mass per unit length is (g =acceleration due to gravity) ____________.
The radius of the orbit of a geostationary satellite is (mean radius of the earth R, angular velocity about an axis in ω and acceleration due to gravity on earth's surface is (g) ______.
In the relation F = `"G M" "m"//"d"^2`, the quantity G
On the earth, a stone is thrown from a height in a direction parallel to the earth’s surface while another stone is simultaneously dropped from the same height. Which stone would reach the ground first and why?
The moon has a mass of 1/81 that of the earth and a radius of 1/4 that of the earth. The escape speed from the surface of the earth is 11.2 km/s. The escape speed from the surface of the moon is ______.
A lift of mass 'm' is connected to a rope which is moving upward with maximum acceleration 'a'. For maximum safe stress, the elastic limit of the rope is 'T'. The minimum diameter of the rope is ______.
(g = gravitational acceleration)
The depth 'd' at which the value of acceleration due to gravity becomes `"I"/"n"` times the value at the earth's surface is ______. (R = radius of earth)
The difference in the acceleration due to gravity at the pole and equator is ______.
(g = acceleration due to gravity, R = radius of the earth; θ = latitude, ω = angular velocity, cos0° = 1, cos90° = 0)
If the surface is smooth, the acceleration of the block m2 will be ______.
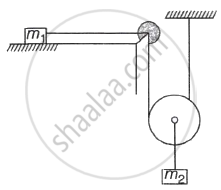
If the change in the value of g at the height h above the surface of the earth is the same as at a depth x below it, then ______.
(both x and h being much smaller than the radius of the earth)
