Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does type of overlap given in the following figure not result in bond formation?
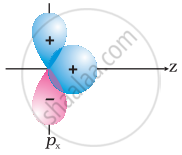 |
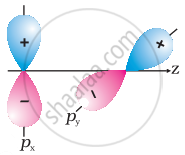 |
Solution
In the first figure given above, the area which is under ++ overlapping is equal to the area under +– overlap. Both the overlaps cancel out with each other as they are oppositely charged. Due to cancelling out of the overlaps the net overlap will be zero.
In the second figure given above, both the p-orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Due to the `p_x, p_y` orbitals being perpendicular with each other, no overlap will be possible.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Mention the steps involved in Hybridization.
Which one of the following is the likely bond angles of sulphur tetrafluoride molecule?
According to Valence bond theory, a bond between two atoms is formed when ______.
In ClF3, NF3 and BF3 molecules the chlorine, nitrogen and boron atoms are ______.
Which bond is stronger σ or π? Why?
Considering x-axis as the molecular axis which out of the following will form a sigma bond.
2px and 2py
Considering x-axis as the molecular axis which out of the following will form a sigma bond.
1s and 2pz
Which of the following molecule contain 50% p-character of hybrid orbital in C atom?
The number of sigma bonds in paracetamol is ____________.
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) | \[\ce{PCl5}\] | (i) | Square pyramidal |
| (b) | \[\ce{SF6}\] | (ii) | Trigonal planar |
| (c) | \[\ce{BrF5}\] | (iii) | Octahedral |
| (d) | \[\ce{BF3}\] | (iv) | Trigonal bipyramidal |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
