Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain why \[\ce{PCl5}\] is trigonal bipyramidal whereas \[\ce{IF5}\] is square pyramidal.
Solution
\[\ce{PC15}\] – The ground state and the excited state outer electronic configurations of phosphorus \[\ce{(Z = 15)}\] are represented below:
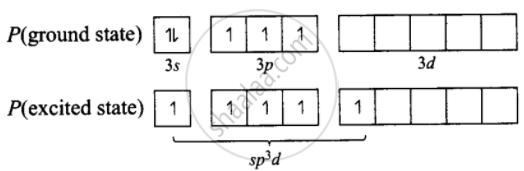
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{Cl}\phantom{..}\ce{Cl}\\
\phantom{.}\backslash\phantom{.}|\phantom{}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{P - Cl}\\
\phantom{.}/\phantom{.}|\phantom{}\\
\ce{Cl}\phantom{..}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use molecular orbital theory to explain why the Be2 molecule does not exist.
Stable form of C may be represented by the formula:
The molecular formula of the compound formed from \[\ce{B}\] and \[\ce{C}\] will be ______.
The electronic configuration of the outer most shell of the most electronegative element is ______.
Amongst the following elements whose electronic configurations are given below, the one having the highest ionisation enthalpy is ______.
Dimagnetic species are those which contain no unpaired electrons. Which among the following are dimagnetic?
(i) \[\ce{N2}\]
(ii) \[\ce{N^{2-}2}\]
(iii) \[\ce{O2}\]
(iv) \[\ce{O^{2-}2}\]
Explain the shape of \[\ce{BrF5}\].
Which of the following statements is correct?
Molecular orbital electronic configuration for 'X' anion is- KK σ*2s2 σ*2s2 π2px2 π2py2 σ2pz2 π*2px1, the anion 'X' is.
