Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why law of segregation is also called the law of purity of gametes?
Solution
- A diploid organism contains two factors for each trait in its diploid cells and the factors segregate during the formation of gametes.
- The two alleles (contrasting characters) do not mix, alter or dilute each other and the gametes formed are ‘pure’ for the characters which they carry.
- A gamete may carry either a dominant or recessive factor but not both.
Hence, this law is also called the law of purity of gametes.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
___________ is the scientific name of garden pea, which Mendel used for his experiments.
Define the following:
Heterozygous
A family consists of two parents and their five children and the pedigree chart below shows the inheritance of the trait colour blindness .
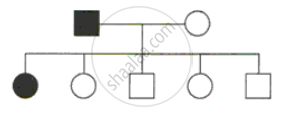
(i) Who is colour blind in parents - Father or Mother?
(ii) How many daughters and sons have beeen born in the family?
(iii) What does the child 1 indicate about this trait?
(iv) Complete the depiction of all probabilities of the trait among the children 2-5 in the chart.
(v) On which chromosome is the gene of this trait located?
(vi) Name one other trait in humans which follows the similar mode of inheritance.
Choose the correct answer:
If a pea plant with round seeds is selfed and the offspring are in the ratio 3:1, then the plant is _________
If a pure tall plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant, then offspring will be ______.
Give Reason:
Discontinuous variations are inheritable.
Give Technical Term:
The hereditary unit, which is responsible for inheritance.
Identify the percentage of recombinants in F2 generation in the following case.
In Morgan's experiment with Drosophila, the yellow-bodied white-eyed female was crossed with a brown-bodied red-eyed male and their F1 progeny were intercrossed.
When two genetic loci produce identical phenotypes in cis and trans position, they are considered to be ______.
It is sometimes observed that the F1 progeny has a phenotype that does not resemble either of the two parents and has an intermediate phenotype. Explain by taking a suitable example and working out the cross upto F2 progeny.
