Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Reproduction in Lower and Higher Animals
▶ 3: Inheritance and Variation
4: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
5: Origin and Evolution of Life
6: Plant Water Relation
7: Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition
8: Respiration and Circulation
9: Control and Co-ordination
10: Human Health and Diseases
11: Enhancement of Food Production
12: Biotechnology
13: Organisms and Populations
14: Ecosystems and Energy Flow
15: Biodiversity, Conservation and Environmental Issues
![Balbharati solutions for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 3 - Inheritance and Variation Balbharati solutions for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 3 - Inheritance and Variation - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:429f7f9009264240a77c8945f6342a63.JPG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Inheritance and Variation
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board.
Balbharati solutions for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 3 Inheritance and Variation Exercises [Pages 68 - 69]
Multiple choice question.
Phenotypic ratio of incomplete dominance in Mirabilis jalapa.
2 : 1 : 1
1 : 2 : 1
3 : 1
2 : 2
Multiple choice question.
In a dihybrid cross, F2 generation offsprings show four different phenotypes while the genotypes are _______.
six
nine
eight
sixteen
Multiple choice question.
A cross between an individual with an unknown genotype for a trait with recessive plant for that trait is _______.
back cross
reciprocal cross
monohybrid cross
test cross
Multiple choice question.
When F2 phenotypic and genotypic ratios are the same, then it is an example of _______.
incomplete dominance
complete dominance
multiple alleles
cytoplasmic inheritance
If the centromere is situated near the end of the chromosome, the chromosome is called ______.
metacentric
acrocentric
sub-metacentric
telocentric
Multiple choice question.
Chromosomal theory of inheritance was proposed by _______.
Sutton and Boveri
Watson and Crick
Miller and Urey
Oparin and Halden
Multiple choice question.
If the genes are located in a chromosome as p-q-r-s-t, which of the following gene pairs will have the least probability of being inherited together?
p and q
r and s
s and t
p and s
Find the mismatch pair:
Down’s syndrome = 44 + XY
Turner’s syndrome = 44 + XO
Klinefelter syndrome = 44 + XXY
Super female = 44 + XXX
Multiple choice question.
A colour-blind man marries a woman, who is homozygous for normal colour vision, the probability of their son being colour blind is –
0%
25%
50%
100%
Explain the statement of
Test cross is back cross but back cross is not necessarily a test cross.
Explain the statement of Law of dominance is not universal.
Define the following term:
Dihybrid cross
Define the following:
Homozygous
Define the following:
Heterozygous
Define the following:
test cross.
Very Short Answer Question.
What is allosome?
Very Short Answer Question.
What is crossing over?
Very Short Answer Question.
Give one example of the autosomal recessive disorder.
What are X-linked genes?
Very Short Answer Question.
What are holandric traits?
Very Short Answer Question.
Give an example of a chromosomal disorder caused due to nondisjunction of autosomes.
Very Short Answer Question.
Give one example of complete sex linkage?
Short Answer Question.
Short Answer Question.
Enlist seven traits of pea plant selected/ studied by Mendel.
Why law of segregation is also called the law of purity of gametes?
Short Answer Question.
Write a note on pleiotropy.
Short Answer Question.
What are the reasons for Mendel’s success?
Short Answer Question.
“Father is responsible for determination of sex of child and not the mother”. Justify.
What is a linkage? How many linkage groups do occur in human being?
Short Answer Question.
Write note on –PKU.
Compare X chromosome and Y chromosome.
Short Answer Question.
Explain the chromosomal theory of inheritance.
Short Answer Question.
Observe the given pedigree chart and answer the following question.
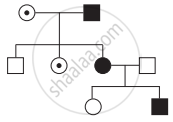
Identify whether the trait is sex-linked or autosomal.
Short Answer Question.
Observe the given pedigree chart and answer the following question.

Give an example of a trait in human beings which shows such a pattern of inheritance.
Match the column-I with column-II and re-write the matching pairs.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| 1. 21 trisomy | a. Turner’s syndrome |
| 2. X-monosomy | b. Klinefelter’s syndrome |
| 3. Holandric traits | c. Down's syndrome |
| 4. Feminized male | d. Hypertrichosis |
What is dihybrid cross?
Explain a dihybrid cross with suitable example and checker board method.
Long answer type question.
Explain with suitable example an independent assotrment.
Long answer type question.
Define test cross and explain its significance.
What is parthenogenesis?
Explain the haplo-diploid method of sex determination in the honey bee.
Long answer type question.
In the answer for inheritance of X-linked genes, Madhav had shown carrier male. His answer was marked incorrect. Madhav was wondering why his marks were cut. Explain the reason.
With the help of a neat labelled diagram, describe the structure of chromosome.
What is cris-cross inheritance?
Long answer type question.
Explain cris-cross inheritance with suitable example.
Long answer type question.
Describe the different types of chromosomes.
Solutions for 3: Inheritance and Variation
![Balbharati solutions for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 3 - Inheritance and Variation Balbharati solutions for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 3 - Inheritance and Variation - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-12-standard-hsc-maharashtra-state-board_6:429f7f9009264240a77c8945f6342a63.JPG)
Balbharati solutions for Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 3 - Inheritance and Variation
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 3 (Inheritance and Variation) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 3 Inheritance and Variation are Heredity or Inheritance, Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics, Back Cross and Test Cross, Deviations from Mendel’s Findings, Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity, Linkage and Crossing Over, Autosomal Inheritance, Sex Linked Inheritance, Sex Determination, Genetic Disorders, Genes and Genetic, Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity.
Using Balbharati Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions Inheritance and Variation exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Inheritance and Variation Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
