Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
Solution 1
The logistic population growth curve is commonly observed in yeast cells that are grown under laboratory conditions. It includes five phases: the lag phase, positive acceleration phase, exponential phase, negative acceleration phase, and stationary phase.
(a) Lag phase: Initially, the population of the yeast cell is very small. This is because of the limited resource present in the habitat.
(b) Positive acceleration phase: During this phase, the yeast cell adapts to the new environment and starts increasing its population. However, at the beginning of this phase, the growth of the cell is very limited.
(c) Exponential phase: During this phase, the population of the yeast cell increases suddenly due to rapid growth. The population grows exponentially due to the availability of sufficient food resources, constant environment, and the absence of any interspecific competition. As a result, the curve rises steeply upwards.
(d) Negative acceleration phase: During this phase, the environmental resistance increases and the growth rate of the population decreases. This occurs due to an increased competition among the yeast cells for food and shelter.
(e) Stationary phase: During this phase, the population becomes stable. The number of cells produced in a population equals the number of cells that die. Also, the population of the species is said to have reached nature’s carrying-capacity in its habitat.

A Verhulst−pearl logistic curve is also known as an S-shaped growth curve.
Solution 2
The S-shaped growth curve is also called a logistic growth curve. It describes a situation in which (in a new environmental condition) the population density of an organism increases slowly establishing itself then increasing rapidly, approaching an exponential growth rate. Many population of micro-organisms broadly follow this basic sigmoidal pattern. For example, when a fresh culture medium is inoculated with bacteria, sigmoidal or S-shaped growth curve is observed. The S-shaped curve is generated when a population approaches the environmental’s carrying capacity. Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals of a population that can be supported in a given time.

The S-shaped growth form is represented by the following equation- ” dNldt = rN[K-NIK] Where, r = intrinsic rate of natural increase N = population density at time t K = carrying capacity
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If 8 individuals in a population of 80 butterflies die in a week, calculate the death rate of the population of butterflies during that period.
Examine the following statement and correct the incorrect one.
There is an adverse impact on manpower in the regions of out-migration.
Answer the following question.
Compare, giving reasons, the J-shaped and S-shaped models of population growth of a species.
What are the three components of population change?
What is the impact of migration?
How did science and technology help in population growth?
Which one of the following is not a component of population change?
Which of the following is not a push factor for migration?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:
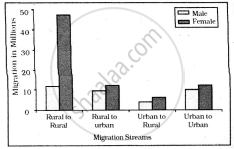
Intra-state Migration by place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
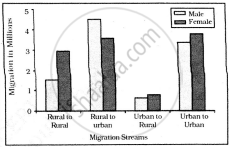
Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
Who dominates the intra-state migration of short distances?
The number of mice in a laboratory was 100 on a particular day. After one year their number increased to 120. Calculate the growth rate in the population.
On the basis of the demographic data of a country given below, construct an age pyramid and explain whether the population is stable, declining or growing.
| Age group | No. of individuals |
| Pre-reproductive | 20,000 |
| Reproductive | 15,000 |
| Post-reproductive | 10,000 |
Exponential growth in plants win be expressed as ______.
Which of the following statement is true?
(i) CBR = Bi/P × 1000
(ii) COR = D /P × 1000
(iii) If birth rate is more than death rate, then CBR results in positive growth of population.
Consider the following and choose the correct answer with the help of given codes-
| STAGES OF POPULATION | GROWTH FEATURES |
| I Period between 1901 to 1921 | 1. Period of steady growth |
| II Period between 1921 to 1951 | 2. Phase of stagnant growth of Population |
| III Period between 1951 to 1981 | 3. High but decreasing growth rate |
| IV After 1981 till present | 4. Period of population explosion |
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
Assertion (A): The population of a region does not change.
Reasoning (R): Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
A : Population of a region does not change.
R : Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Assertion: Population of a region does not change.
Reason: Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Assertion: Population of a region does not change.
Reasoning: Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
