Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With reference to the photoelectric effect, define threshold wavelength
Solution
Maximum wavelength of incident radiation required to eject the electron from photo sensitive surface.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When radiations of wavelength λ1 and λ2 are incident on certain photosensitive, such that E1 > E2 . Then Planck's constant 'h' is ......................... .
(C = Velocity of light).
Find the wave number of a photon having energy of 2.072 eV
Given : Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C,
Velocity of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s.
Write Einstein's photoelectric equation and mention which important features in photoelectric effect can be explained with the help of this equation.
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons gets doubled when the wavelength of light incident on the surface changes from λ1 to λ2. Derive the expressions for the threshold wavelength λ0 and work function for the metal surface.
The slope of frequency of incident light and stopping potential for a given surface will be
What will be wavelength of a photon of momentum 6.6 × 10–24 kgms–1?
Which of the following is/are true for cathode ray
The wavelength of matter is independent of
(i) A ray of light incident on face AB of an equilateral glass prism, shows minimum deviation of 30°. Calculate the speed of light through the prism.
(ii) Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
- Calculate the energy and momentum of a photon in a monochromatic beam of wavelength 331.5 nm.
- How fast should a hydrogen atom travel in order to have the same momentum as that of the photon in part (a)?
The graphs below show the variation of the stopping potential VS with the frequency (ν) of the incident radiations for two different photosensitive materials M1 and M2.
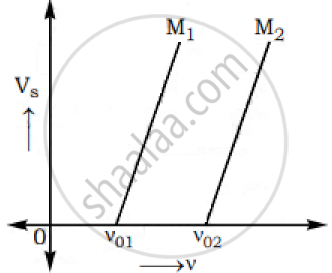
Express work function for M1 and M2 in terms of Planck’s constant(h) and Threshold frequency and charge of the electron (e).
If the values of stopping potential for M1 and M2 are V1 and V2 respectively then show that the slope of the lines equals to `(V_1-V_2)/(V_(01)-V_(02))` for a frequency,
ν > ν02 and also ν > ν01
