Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the structures and names of the compounds formed when compound ‘A’ with molecular formula, \[\ce{C7H8}\] is treated with \[\ce{Cl2}\] in the presence of \[\ce{FeCl3}\].
Solution
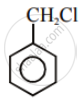
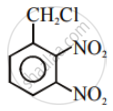
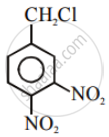
The compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H8}\] is toluene, \[\ce{C6H5CH3}\]. Since \[\ce{^-CH3}\] group is o-, p-directing, therefore, chlorination of toluene gives o-chlorotoluene and p-chlorotoluene, in which the p-isomer predominates.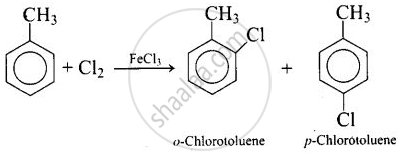
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is ____________.
Among the following, the dissociation constant is highest for:
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism?
Which of the following compounds will give a racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH ion?
1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H9Br}\] is treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and \[\ce{KOH}\] both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
How do polar solvents help in the first step in SN1 mechanism?
The decreasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is ______.
Complete the reaction with the main product formed:

An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.