Advertisements
Advertisements
Draw a typical input and output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Show how these characteristics can be used to determine (a) the input resistance (r1), and (b) current amplification factor (β)
Concept: Transistor and Characteristics of a Transistor
Four nuclei of an element undergo fusion to form a heavier nucleus, with release of energy. Which of the two – the parent or the daughter nucleus – would have higher binding energy per nucleon?
Concept: Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
Give three reasons why modulation of a message signal is necessary for long-distance transmission
Concept: Need for Modulation and Demodulation
Show graphically an audio signal, a carrier wave and an amplitude modulated wave
Concept: Need for Modulation and Demodulation
A carrier wave of peak voltage 15 V is used to transmit a message signal. Find the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to have a modulation index of 60%
Concept: Modulation and Its Necessity
Three-point charges q, – 4q and 2q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 'l' as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the magnitude of the resultant electric force acting on the charge q

(b) Find out the amount of the work done to separate the charges at infinite distance.
Concept: Coulomb’s Law - Force Between Two Point Charges
In a potentiometer arrangement for determining the emf of a cell, the balance point of the cell in open circuit is 350 cm. When a resistance of 9 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 300 cm. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
Concept: Cells, Emf, Internal Resistance
Using the concept of free electrons in a conductor, derive the expression for the conductivity of a wire in terms of number density and relaxation time. Hence obtain the relation between current density and the applied electric field E.
Concept: Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
Concept: Moving Coil Galvanometer
State Ampere’s circuital law.
Concept: Ampere’s Circuital Law
Define mutual inductance.
Concept: Inductance > Mutual Inductance
What do you understand by the statement, "Electromagnetic waves transport momentum"?
Concept: Electromagnetic Spectrum
A point charge q is at a distance of d/2 directly above the centre of a square of side d, as shown the figure. Use Gauss' law to obtain the expression for the electric flux through the square.
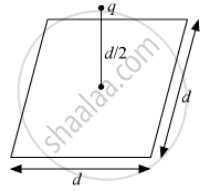
Concept: Applications of Gauss’s Law
Draw a necessary arrangement for winding of primary and secondary coils in a step-up transformer. State its underlying principle and derive the relation between the primary and secondary voltages in terms of number of primary and secondary turns. Mention the two basic assumptions used in obtaining the above relation.
Concept: Inductance > Mutual Inductance
State Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
Concept: Faraday’s Law of Induction
How are electromagnetic waves produced?
Concept: Electromagnetic Waves
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Concept: Polarisation
Draw graphs showing variation of photoelectric current with applied voltage for two incident radiations of equal frequency and different intensities. Mark the graph for the radiation of higher intensity.
Concept: Experimental Study of Photoelectric Effect
Draw the necessary energy band diagrams to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
How does the change in temperature affect the behaviour of these materials ? Explain briefly.
Concept: Energy Bands in Conductors, Semiconductors and Insulators
