Advertisements
Advertisements
A shopkeeper bought an article for Rs. 3,450. He marks the price of the article 16% above the cost price. The rate of sales tax charged in the article is 10%
Find the:
1) market price of the article.
2) price paid by a customer who buys the article
Concept: undefined > undefined
Without using trigonometric tables evaluate:
`(sin 65^@)/(cos 25^@) + (cos 32^@)/(sin 58^@) - sin 28^2. sec 62^@ + cosec^2 30^@`
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
The marks obtained by 30 students in a class assignment of 5 marks are given below.
| Marks | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| No. of Students |
1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
Calculate the mean, median and mode of the above distribution
Concept: undefined > undefined
Find the value of ‘K’ for which x = 3 is a solution of the quadratic equation
`(K + 2)x^2 - kx + 6 = 0`
Concept: undefined > undefined
Construct a regular hexagon of side 5 cm. Construct a circle circumscribing the hexagon. All traces of construction must be clearly shown.
Concept: undefined > undefined
If a, b, c are in continued proportion, prove that (a + b + c) (a – b + c) = a2 + b2 + c2
Concept: undefined > undefined
A wholesaler buys a TV from the manufacturer for Rs. 25,000. He marks the price of TV 20% above his cost price and sells it to a retailer at a 10% discount on the market price. If the rate of the VAT is 8%, find the :
1) Market price
2) Retailer’s cost price inclusive of tax.
3) VAT paid by the wholesaler.
Concept: undefined > undefined
ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠ABC = 90°. D is any point on AB and DE is perpendicular to AC. Prove that :
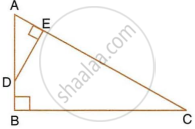
- ΔADE ∼ ΔACB.
- If AC = 13 cm, BC = 5 cm and AE = 4 cm. Find DE and AD.
- Find, area of ΔADE : area of quadrilateral BCED.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Sum of two natural numbers is 8 and the difference of their reciprocal is `2/15`. Find the numbers.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Calculate the ratio in which the line joining A(−4, 2) and B(3, 6) is divided by point P(x, 3). Also, find
- x
- length of AP.
Concept: undefined > undefined
The numbers 6, 8, 10, 12, 13 and x are arranged in an ascending order. If the mean of the observations is equal to the median, find the value of x
Concept: undefined > undefined
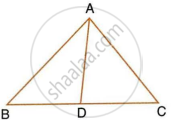
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠DAC, AB = 8 cm, AC = 4 cm and AD = 5 cm.
- Prove that ΔACD is similar to ΔBCA.
- Find BC and CD.
- Find area of ΔACD : area of ΔABC.
Concept: undefined > undefined
If (x - 9) : (3x + 6) is the duplicate ratio of 4: 9, find the value of x.
Concept: undefined > undefined
At what rate % p.a. will a sum of Rs. 4000 yield Rs. 1324 as compound interest in 3 years?
Concept: undefined > undefined
The median of the following observations
11, 12, 14, (x - 2), (x + 4), (x + 9), 32, 38, 47 arranged in ascending order is 24.
Find the value of x and hence find the mean.
Concept: undefined > undefined
If (x – 2) is a factor of the expression 2x3 + ax2 + bx – 14 and when the expression is divided by (x – 3), it leaves a remainder 52, find the values of a and b.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Solve the following equation and calculate the answer correct to two decimal places:
x2 – 5x – 10 = 0.
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendicular to BC.
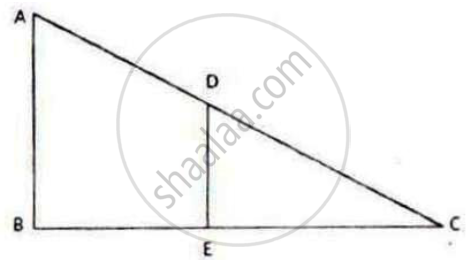
1) Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔDEC
2) If AB = 6 cm; DE = 4 cm and AC = 15 cm. Calculate CD.
3) Find the ratio of area of ΔABC: area of ΔDEC
Concept: undefined > undefined
Without solving the following quadratic equation, find the value of ‘p' for which the given equation has real and equal roots:
x2 + (p – 3)x + p = 0.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A shopkeeper purchases a certain number of books for Rs. 960. If the cost per book was Rs. 8 less, the number of books that could be purchased for Rs. 960 would be 4 more. Write an equation, taking the original cost of each book to be Rs. x, and solve it to find the original cost of the books.
Concept: undefined > undefined
