Advertisements
Chapters
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 7 - Motion NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 7 - Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:8626690beaa343fd99329119ec507003.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Motion
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CBSE NCERT for Science [English] Class 9.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 7 Motion Intext question [Pages 74 - 83]
An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example.
A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds?
Which of the following is true for displacement?
- It cannot be zero.
- Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed?
What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes. What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is, 3 × 108m s−1.
When will you say a body is at uniform acceleration?
When will you say a body is at non-uniform acceleration?
A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h−1 to 60 km h−1 in 5 s. Find the acceleration of the bus.
A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed 40 km h−1 in 10 minutes. Find its acceleration.
What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
What can you say about the motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
What is the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity-time graph?
A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.1 m s-2 for 2 minutes. Find
- the speed acquired
- the distance travelled.
A train is travelling at a speed of 90 km h−1. Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of −0.5 m s−2. Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
A trolley, while going down an inclined plane, has an acceleration of 2 cm s−2. What will be its velocity 3 s after the start?
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 m s−2. What distance will it cover in 10 s after start?
A stone is thrown in a vertically upward direction with a velocity of 5 m s-1. If the acceleration of the stone during its motion is 10 m s-2 in the downward direction, what will be the height attained by the stone and how much time will it take to reach there?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 7 Motion Exercises [Pages 85 - 86]
An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 40 s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2 minutes 20 s?
Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight 300 m road in 2 minutes 30 seconds and then turns around and jogs 100 m back to point C in another 1 minute. What are Joseph’s average speeds and velocities in jogging?
- from A to B and
- from A to C?
Abdul, while driving to school, computes the average speed for his trip to be 20 km h−1. On his return trip along the same route, there is less traffic and the average speed is 30 km h−1. What is the average speed for Abdul’s trip?
A motorboat starting from rest on a lake accelerates in a straight line at a constant rate of 3.0 m s−2 for 8.0 s. How far does the boat travel during this time?
A driver of a car travelling at 52 km h−1 applies the brakes and accelerates uniformly in the opposite direction. The car stops in 5 s. Another driver going at 3 km h−1 in another car applies his brakes slowly and stops in 10 s. On the same graph paper, plot the speed versus time graphs for the two cars. Which of the two cars travelled farther after the brakes were applied?
Given figure shows the distance-time graph of three objects A, B and C. Study the graph and answer the following questions:
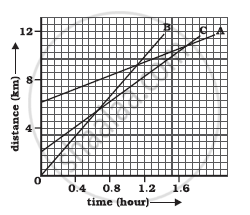
- Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
- Are all three ever at the same point on the road?
- How far has C travelled when B passes A?
- How far has B travelled by the time it passes C?
A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 m s−2, with what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground?
The speed-time graph for a car is shown in the following figure:
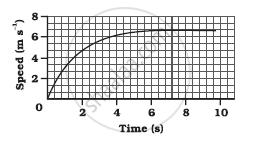
- Find how far the car travels in the first 4 seconds. Shade the area on the graph that represents the distance travelled by the car during the period.
- Which part of the graph represents uniform motion of the car?
State which of the following situation is possible and give an example:
An object with a constant acceleration but with zero velocity.
State which of the following situation is possible and give an example:
An object moving with an acceleration but with uniform speed.
State which of the following situation is possible and give an example:
An object moving in a certain direction with an acceleration in the perpendicular direction.
An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius 42250 km. Calculate its speed if it takes 24 hours to revolve around the earth.
Solutions for 7: Motion
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 7 - Motion NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 7 - Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:8626690beaa343fd99329119ec507003.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 7 - Motion
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE 7 (Motion) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 9 chapter 7 Motion are Motion and Rest, Motion Along a Straight Line, Types of Motion, Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction, Rate of Change of Velocity, Describing Motion, Distance and Displacement, Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph, Velocity - Time Graphs, Equations of Motion by Graphical Method, Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method, Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method, Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Motion (Numerical), Motion and Rest, Motion Along a Straight Line, Types of Motion, Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction, Rate of Change of Velocity, Describing Motion, Distance and Displacement, Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph, Velocity - Time Graphs, Equations of Motion by Graphical Method, Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method, Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method, Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Motion (Numerical).
Using NCERT Science [English] Class 9 solutions Motion exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Motion Science [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
