Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:8626690beaa343fd99329119ec507003.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CBSE NCERT for Science [English] Class 9.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Intext question [Pages 3 - 10]
Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, lemon water, smell of perfume.
Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
(density = mass/volume).
Arrange the following in order of increasing density-
air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
Comment upon the following:
rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Give reasons:
A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
Give reasons:
A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Give reasons:
A wooden table should be called a solid.
Give reasons:
We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
300 K
Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
573 K
What is the physical state of water at 250°C.
What is the physical state of water at 100ºC?
For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
How does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Exercises [Page 12]
Convert the following temperature to the celsius scale.
293 K
Convert the following temperature to the celsius scale.
470 K
Convert the following temperature to the Kelvin scale.
25°C
Convert the following temperature to the Kelvin scale.
373°C
Give a reason for the following observation.
Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
Give a reason for the following observation.
We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between particles -
water, sugar, oxygen
What is the physical state of water at 25°C.
What is the physical state of water at 0°C.
What is the physical state of water at 100°C.
Give two reasons to justify water at room temperature is a liquid.
Give two reasons to justify an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
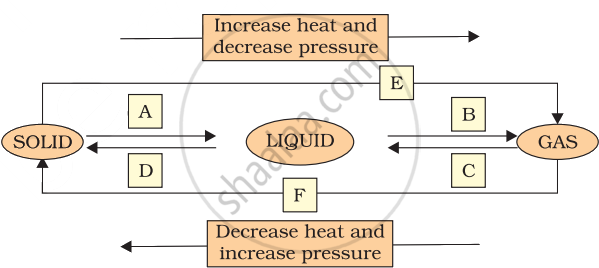
Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Group Activity [Page 13]
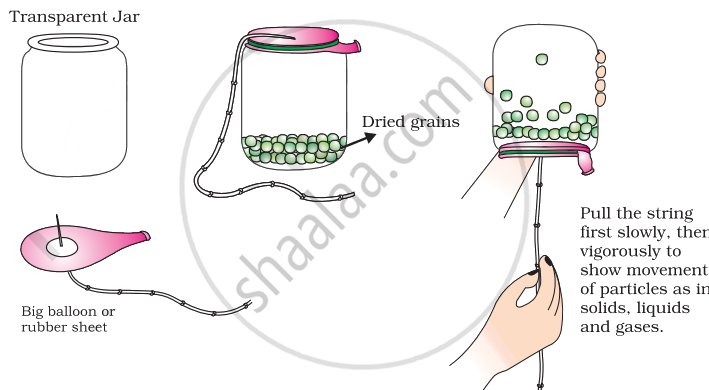
Prepare a model to demonstrate movement of particles in solids, liquids and gases.
For making this model you will need
- A transparent jar
- A big rubber balloon or piece of stretchable rubber sheet
- A string
- Few chickpeas or black gram or dry green peas.
How to make?
- Put the seeds in the jar.
- Sew the string to the centre of the rubber sheet and put some tape to keep it tied securely.
- Stretch and tie the rubber sheet on the mouth of the jar.
- Your model is ready. Now run your fingers up and down the string by first tugging at it slowly and then rapidly.
Solutions for 1: Matter in Our Surroundings
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:8626690beaa343fd99329119ec507003.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE 1 (Matter in Our Surroundings) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 9 chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings are Heat and change of physical state, Matter (Substance), Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter, The Solid State, The Liquid State, The Gaseous State, Plasma, Concept of Melting (Fusion), Concept of Boiling (Vaporization), Concept of Evaporation, Bose-einstein Condensate, Concept of Sublimation, Concept of Freezing (Solidification), Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction), Concept of Desublimation (Deposition), Heat and change of physical state, Matter (Substance), Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter, The Solid State, The Liquid State, The Gaseous State, Plasma, Concept of Melting (Fusion), Concept of Boiling (Vaporization), Concept of Evaporation, Bose-einstein Condensate, Concept of Sublimation, Concept of Freezing (Solidification), Concept of Condensation (Liquefaction), Concept of Desublimation (Deposition).
Using NCERT Science [English] Class 9 solutions Matter in Our Surroundings exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Matter in Our Surroundings Science [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
