Topics
Heredity and Evolution
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Protein Synthesis
- Transcription, Translation and Translocation
- Protein Synthesis
- Protein Synthesis
- Organic Evolution
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Evolution and Classiffication
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Darwinism
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Speciation
- Human Evolution
Life Processes in Living Organisms Part -1
- Living Organisms and Life Processes
- Living Organism and Energy Production
- Formation of ATP
- Energy Production in Living Organism
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
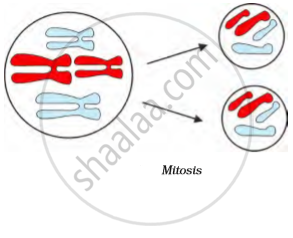
- Mitosis and Its Phases
- Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus)
- Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm)
- Significance of Mitosis
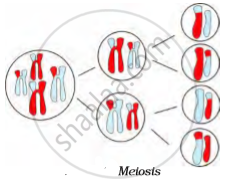
- Meiosis as a Reduction Division
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II
- Significance of Meiosis
- Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
- Introduction to Life Processes in Living Organisms
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Fission
- Fragmentation
- Regeneration
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Reproduction and Modern Technology
- Reproductive Health
Environmental Management
- Our needs and the Environment
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Relationship Between Environment and Ecosystem
- Environmental Balance
- Environmental Conservation
- Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity
- Endangered Species
Towards Green Energy
- Energy and Use of Energy
- Generation of Electrical Energy
- Heat Energy (Thermal Energy)
- Nuclear Energy
- Natural Gas Energy
- Electric Energy Generation and Environment
- Hydroelectric Energy
- Wind Energy
- Solar Energy
- Solar Energy
Animal Classification
- Biological Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- New Criteria for Basis of Classification
- History of Animal Classification
- Traditional Method of Animal Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Phylum: Aschelminthes
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Phylum: Hemichordata
- Phylum: Chordata
- Kingdom Animalia
- Chordata: Vertebrata
Introduction to Microbiology
- Microorganisms (Microbes) and Microbiology
- Applied Microbiology
- Industrial Microbiology
- Useful micro-organisms
Cell Biology and Biotechnology
- Cell Biology (Cytology)
- Stem Cells
- Organ Transplantation
- Organ and Body Donation
- Biotechnology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Modern Agricultural Practices and Crop Improvement
- Important Stages in Agricultural Development
Social Health
- Social Health
- Factors Disturbing the Social Health
- Communication Media and Excessive Use of Modern Technology
- Stress Management
Disaster Management
- Disaster
- Effects of Disaster
- Nature and Scope of Disaster
- Disaster Management
- Classification of Disaster Management
- Disaster Management Cycle
- Structure of Disaster Management Authority
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Mock Drill
Life's Internal Secrets
The Regulators of Life
- Coordination in Plants - Introduction
- Control and Co-ordination in Plants
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Chemical Control
The Life Cycle
Mapping Our Genes
Striving for Better Environment 2
- Use of Efficient and Eco-friendly Technology
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Enforcement of Acts, Laws and Policies
Understanding Metals and Non-Metals
Amazing World of Carbon Compounds
- Cell Division
- Types of Cell Division
- Amitosis - Direct Division
- Mitosis - Indirect Division
- Meiosis - Reduction Division
- Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
New cells are formed in organisms to grow, to replace old, dead and injured cells, and to form gametes required for reproduction. The process by which new cells are made is called cell division. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. The process of cell division by which most of the cells divide for growth is called mitosis. In this process, each cell called the mother cell, divides to form two identical daughter cells.
The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell. It helps in the growth and repair of tissues in organisms.
Specific cells of reproductive organs or tissues in animals and plants divide to form gametes, which give rise to offspring after fertilisation. They divide by a different process called meiosis which involves two consecutive divisions. When a cell divides by meiosis, it produces four new cells instead of just two. The new cells only have half the number of chromosomes than the mother cells.