Topics
Basic Concepts in Geometry
Angles
Integers
- Concept of Integers
- Concept for Natural Numbers
- Concept for Whole Numbers
- Negative and Positive Numbers
- Representation of Integers on the Number Line
- Addition of Integers
- Concept of Opposite Numbers
- Concept of Comparing Integers
- Subtraction of Integers
Operations on Fractions
- Concept of Fractions
- Conversion Between Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
- Addition of Fraction
- Subtraction of Fraction
- Fraction on the Number Line
- Multiplication of Fraction
- Concept of Reciprocal or Multiplicative Inverse
- Division of Fractions
Decimal Fractions
Bar Graphs
Symmetry
Divisibility
HCF-LCM
Equations
Ratio and Proportion
Percentage
Profit –Loss
Banks and Simple Interest
Triangles and Their Properties
Quadrilaterals
Geometrical Constructions
- Perpendicular Lines
- Drawing a Perpendicular to a Line at a Point on the Line
- Drawing a perpendicular to a line from a point outside the line
- The Perpendicular Bisector
- Drawing the perpendicular bisector of a segment using a compass.
- Carl Gauss’s Clever Trick
Three Dimensional Shapes
Notes
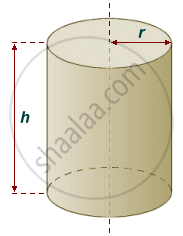
Concept of Cylinder:
- A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two round shapes at either end and two parallel lines connecting the round ends. Bases are always parallel and congruent to each other.
- A closed cylinder has two flat circular faces and one curved face.
- The cylinder has two circular edges and no vertex.
Type of Cylinder:
There are two types of cylinder:
1. Right Circular Cylinder:
When the two bases of the cylinder are over each other in the exact position and the axis is at the right angle to the base, it is called the cylinder is a right cylinder.
If the bases are circular in shape, then it is called a Right circular cylinder.
If the bases are in an elliptical shape, then it is called an Elliptical Cylinder.
2. Oblique Cylinder:
When one of the bases of the cylinder is sideways and the axis is not a right angle to the base, then it is an oblique cylinder.

Properties of Cylinder:
- A cylinder has only one curved side.
- A cylinder has two identical flat ends that are circular or elliptical.
- The bases are always congruent and parallel.
- It is similar to the prism since it has the same cross-section everywhere.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Shaalaa.com | Concept of Cylinder
to track your progress
