Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 60 µF capacitor is connected to a 110 V, 60 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
उत्तर
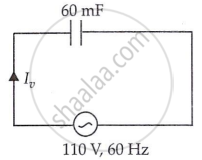
Capacitance of capacitor, C = 60 μF = 60 × 10−6 F
Supply voltage, V = 110 V
Frequency, f = 60 Hz
Angular frequency, ω = 2πr
Capacitive reactance Xc = `1/(ω"C")`
= `1/(2pi "fC")`
= `1/(2 xx 3.14 xx 60 xx 60 xx 10^-6)`
= 44.2 Ω
The rms value of current is given as:
`"I" = "V"/"X"_"c"`
= `110/44.2`
= 2.49 A
Hence, the rms value of the current is 2.49 A.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive the relationship between the peak and the rms value of current in an a.c. circuit.
In a series RL circuit, the resistance and inductive reactance are the same. Then the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is
An inductor 20 mH, a capacitor 50 μF and a resistor 40Ω are connected in series across a source of emf V = 10 sin 340 t. The power loss in AC circuit is
How will you define RMS value of an alternating current?
Define electric resonance.
Obtain an expression for average power of AC over a cycle. Discuss its special cases.
Predict the polarity of the capacitor in a closed circular loop when two bar magnets are moved as shown in the figure.

A capacitor is used in the primary circuit of an induction coil.
Why is choke coil needed in the use of fluorescent tubes with ac mains? Why can we not use an ordinary resistor instead of the choke coil?
The rms current Irms is related to the peak current Io as ______.
The capacitive reactance in an A.C. circuit is ______.
An alternating voltage source of variable angular frequency ‘w’ and fixed amplitude ‘V’ is connected in series with a capacitance C and electric bulb of resistance R(inductance zero). When ‘w’ is increased ______.
For a series LCR circuit, I vs ω curve is shown:
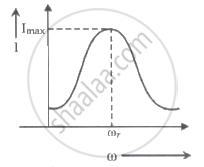
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly capacitive.
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly inductive.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is equal to the resistance of the circuit.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is 0.
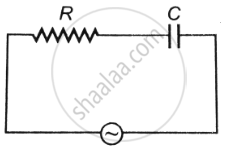
A 50 Hz AC source of 20 volts is connected across R and C as shown in figure. The voltage across R is 12 volt. The voltage across c is ______.
A series CR circuit with R = 200 Ω and C = (50/π) µF is connected across an ac source of peak voltage ε0 = 100 V and frequency v = 50 Hz. Calculate (a) impedance of the circuit (Z), (b) phase angle (Φ), and (c) voltage across the resistor.
Draw graphs showing the variations of inductive reactance and capacitive reactance with the frequency of the applied ac source.
A 220V, 50Hz ac source is connected to a coil having coefficient of self-induction of 1H and a resistance of 400 Ω. Calculate:
- the reactance of the coil.
- the impedance of the coil.
- the current flowing through the coil.
