Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball is dropped and its displacement vs time graph is as shown figure (displacement x is from ground and all quantities are +ve upwards).

- Plot qualitatively velocity vs time graph.
- Plot qualitatively acceleration vs time graph.
उत्तर
To calculate velocity we will find the slope which is calculated by `(dx)/(dt)` for the displacement-time curve and to find acceleration we will find slope `(dV)/(dt)` of the velocity-time curve.
Sign convention: We are taking downward as negative and upward as positive.
The ball is bouncing on the ground and it is clear from the graph that displacement x is positive throughout. The ball is dropped from a height and its velocity increases in a downward direction due to gravity pull. In this condition v is negative but the acceleration of the ball is equal to the acceleration due to gravity i.e, a = – g. When the ball rebounds in the upward direction its velocity is positive but acceleration is a = – g.
a. The velocity-time graph of the ball is shown in figure.
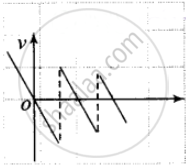
b. The acceleration-time graph of the ball os shown in figure.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
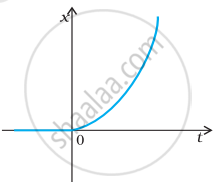
The figure shows the x-t plot of one-dimensional motion of a particle. Is it correct to say from the graph that the particle moves in a straight line for t < 0 and on a parabolic path for t > 0? If not, suggest a suitable physical context for this graph.
A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km h–1 fires a bullet at a thief’s car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of 192 km h–1. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is 150 m s–1, with what speed does the bullet hit the thief’s car? (Note: Obtain that speed which is relevant for damaging the thief’s car).
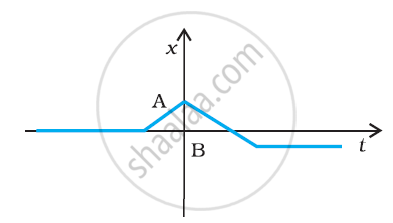
Suggest a suitable physical situation for the following graphs:
A particle moves along the X-axis as x = u (t − 2 s) + a (t − 2 s)2.
(a) the initial velocity of the particle is u
(b) the acceleration of the particle is a
(c) the acceleration of the particle is 2a
(d) at t = 2 s particle is at the origin.
A particle starts from the origin, goes along the X-axis to the point (20 m, 0) and then return along the same line to the point (−20 m, 0). Find the distance and displacement of the particle during the trip.
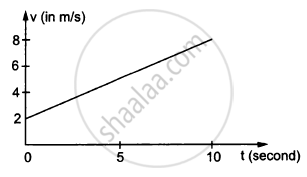
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the distance travelled in 0 to 10s
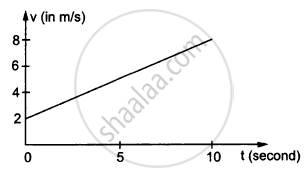
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the displacement in 0 to 10 s.
Refer to the graphs in figure. Match the following.
| Graph | Characteristic |
(a) 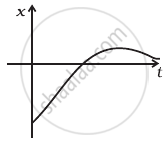 |
(i) has v > 0 and a < 0 throughout. |
(b) 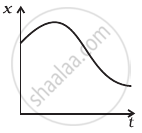 |
(ii) has x > 0 throughout and has a point with v = 0 and a point with a = 0. |
(c) 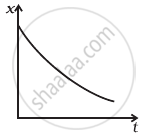 |
(iii) has a point with zero displacement for t > 0. |
(d) 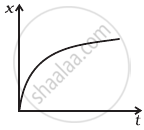 |
(iv) has v < 0 and a > 0. |
Ship A is sailing towards the northeast with velocity `vecv = 30hati + 50hatj` km/hr where `hati` points east and `hatj`, north. Ship B is at a distance of 80 km east and 150 km north of Ship A and is sailing west at 10 km/hr. A will be at the minimum distance from B in ______.
A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at 40 km/h and other half at 60 km/h. The average speed of the car is ______.
