Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0, collides inelastically (e > 0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that for head-on collision, both the balls move forward.
उत्तर
Let v1 and v2 be the velocities of the two balls after a collision.
Now, by the principle of conservation of linear momentum,
2mv0 = mv1 + mv2
or 2v0 = v1 + v2
And e = `(v_2 - v_1)/(2v_0)`
⇒ v2 = v1 + 2v0e
∴ 2v1 = 2v0 – 2ev0
∴ v1 = v0 (1 – e)
Since, e < 1 ⇒ v1 has the same sign as v0, therefore, the ball moves on after collision.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision are the ______ of the system of two bodies.
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact)?
A trolley of mass 200 kg moves with a uniform speed of 36 km/h on a frictionless track. A child of mass 20 kg runs on the trolley from one end to the other (10 m away) with a speed of 4 m s–1 relative to the trolley in a direction opposite to the its motion, and jumps out of the trolley. What is the final speed of the trolley? How much has the trolley moved from the time the child begins to run?
A particle of mass 'm' collides with another stationary particle of mass 'M'. A particle of mass 'm' stops just after collision. The coefficient of restitution is ______.
Two bodies of masses 3 kg and 2 kg collide bead-on. Their relative velocities before and after collision are 20 m/s and 5 m/s respectively. The loss of kinetic energy of the system is ______.
A body of mas 'm' moving with speed 3 m/s collides with a body of mass '2m' at rest. The coalesced mass will start to move with a speed of ______.
Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Iniially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
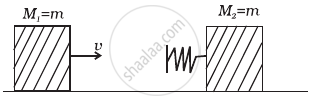
- While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring.
- While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
- If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest.
- If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic.
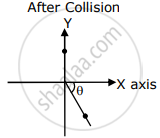
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
Three identical blocks A, B and C are placed on horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks A and C are at rest. But A is approaching towards B with a speed 10 m/s. The coefficient of restitution for all collision is 0.5. The speed of the block C just after the collision is ______.

