Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A boy riding on his bike is going towards east at a speed of 4√2 m s−1. At a certain point he produces a sound pulse of frequency 1650 Hz that travels in air at a speed of 334 m s−1. A second boy stands on the ground 45° south of east from his. Find the frequency of the pulse as received by the second boy.
उत्तर
Given:
Frequency of pulse produced by the bike \[f_0\]= 1650 Hz
Velocity of bike \[v_b\] =4\[\sqrt{2}\]ms−1
Velocity of sound in air v = 334 ms−1
Frequency of pulse received by the second boy \[f\]= ?
Velocity of an observer \[v_0\]= 0
Velocity of source will be : \[v_s = v_b \cos\theta\]
=\[4\sqrt{2} \times \cos {45}^\circ\]
=\[4\sqrt{2} \times \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} = 4 {\text { ms }}^{- 1}\]
Frequency of pulse received by the second boy is given by:
\[f = \left( \frac{v}{v - v_s} \right) f_0 \]
\[ = \left( \frac{334}{334 - 4} \right) \times 1650\]
\[ = 1670 \text { Hz }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The wavelengths of two sound waves in air are `81/173`m and `81/170`m. They produce 10 beats per second. Calculate the velocity of sound in air
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
When two waves with same frequency and constant phase difference interfere,
A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is vibrated with a sonometer wire and 6 beats per second are heard. The beat frequency reduces if the tension in the string is slightly increased. The original frequency of vibration of the string is
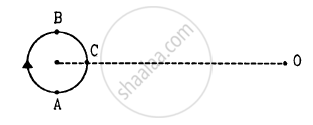
A small source of sounds moves on a circle as shown in figure and an observer is sitting at O. Let \[v_1, v_2, v_3\] be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
A person can hear sound waves in the frequency range 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Find the minimum and the maximum wavelengths of sound that is audible to the person. The speed of sound is 360 m s−1.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
Calculate the bulk modulus of air from the following data about a sound wave of wavelength 35 cm travelling in air. The pressure at a point varies between (1.0 × 105 ± 14) Pa and the particles of the air vibrate in simple harmonic motion of amplitude 5.5 × 10−6 m.
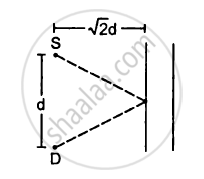
A source S and a detector D are placed at a distance d apart. A big cardboard is placed at a distance \[\sqrt{2}d\] from the source and the detector as shown in figure. The source emits a wave of wavelength = d/2 which is received by the detector after reflection from the cardboard. It is found to be in phase with the direct wave received from the source. By what minimum distance should the cardboard be shifted away so that the reflected wave becomes out of phase with the direct wave?
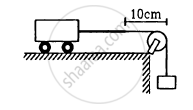
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
The separation between a node and the next antinode in a vibrating air column is 25 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequency of vibration of the air column.
The first overtone frequency of a closed organ pipe P1 is equal to the fundamental frequency of a open organ pipe P2. If the length of the pipe P1 is 30 cm, what will be the length of P2?
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
