Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the bulk modulus of air from the following data about a sound wave of wavelength 35 cm travelling in air. The pressure at a point varies between (1.0 × 105 ± 14) Pa and the particles of the air vibrate in simple harmonic motion of amplitude 5.5 × 10−6 m.
उत्तर
Given:
Wavelength of sound wave
Bulk modulus is given by:
\[B = \left( \frac{14 \times 35 \times {10}^{- 2} m}{2\pi\left( 5 . 5 \right) \times {10}^{- 6} m} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = 1 . 4 \times {10}^5 N/ m^2\]
Hence, the bulk modulus of air is 1.4\[\times\] 105 N/m2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain what is Doppler effect in sound
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is vibrated with a sonometer wire and 6 beats per second are heard. The beat frequency reduces if the tension in the string is slightly increased. The original frequency of vibration of the string is
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Velocity of sound
(c) Wavelength
(d) Time period
The equation of a travelling sound wave is y = 6.0 sin (600 t − 1.8 x) where y is measured in 10−5 m, t in second and x in metre. (a) Find the ratio of the displacement amplitude of the particles to the wavelength of the wave. (b) Find the ratio of the velocity amplitude of the particles to the wave speed.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
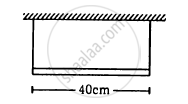
The length of the wire shown in figure between the pulley is 1⋅5 m and its mass is 12⋅0 g. Find the frequency of vibration with which the wire vibrates in two loops leaving the middle point of the wire between the pulleys at rest.
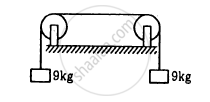
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
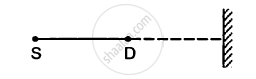
A source of sound S and detector D are placed at some distance from one another. a big cardboard is placed near hte detector and perpendicular to the line SD as shown in figure. It is gradually moved away and it is found that the intensity changes from a maximum to a minimum as the board is moved through a distance of 20 cm. Find the frequency of the sound emitted. Velocity of sound in air is 336 m s−1.
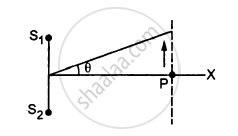
Two speakers S1 and S2, driven by the same amplifier, are placed at y = 1.0 m and y = −1.0 m(See figure). The speakers vibrate in phase at 600 Hz. A man stands at a point on the X-axis at a very large distance from the origin and starts moving parallel to the Y-axis. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1. (a) At what angle θ will the intensity of sound drop to a minimum for the first time? (b) At what angle will he hear a maximum of sound intensity for the first time? (c) If he continues to walk along the line, how many more can he hear?
Two coherent narrow slits emitting sound of wavelength λ in the same phase are placed parallel to each other at a small separation of 2λ. The sound is detected by moving a detector on the screen ∑ at a distance D(>>λ) from the slit S1 as shown in figure. Find the distance x such that the intensity at P is equal to the intensity at O.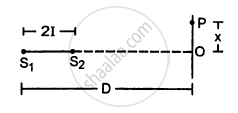
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
Two electric trains run at the same speed of 72 km h−1 along the same track and in the same direction with separation of 2.4 km between them. The two trains simultaneously sound brief whistles. A person is situated at a perpendicular distance of 500 m from the track and is equidistant from the two trains at the instant of the whistling. If both the whistles were at 500 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequencies heard by the person.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A source of sound emitting a 1200 Hz note travels along a straight line at a speed of 170 m s−1. A detector is placed at a distance 200 m from the line of motion of the source. (a) Find the frequency of sound receive by the detector at the instant when the source gets closest to it. (b) Find the distance between the source and the detector at the instant in detects the frequency 1200 Hz. Velocity of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
During propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave ______.
- all the particles are vibrating in the same phase.
- amplitude of all the particles is equal.
- particles of the medium executes S.H.M.
- wave velocity depends upon the nature of the medium.
In an experiment to determine the velocity of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube, the first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm for a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The velocity of the sound at room temperature is 336 ms-1. The third resonance is observed when the air column has a length of ______ cm.
A small speaker delivers 2W of audio output. At what distance from the speaker will one detect 120 dB intensity sound?
[Given reference intensity of sound as 10-12W/m2]
