Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
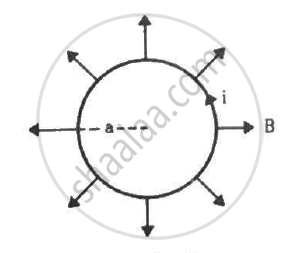
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
उत्तर
Given:-
A circular loop of radius = a
So, the length of the loop, l = 2πa
Electric current through the loop = i
As per the question,
The loop is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field. The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B
Therefore, the magnetic field points radially outwards.
Here, the angle between the length of the loop and the magnetic field, θ = 90˚
Magnetic force is given by
`|vecF| = iveclxx vecB`
`vecF = i(2piaxxvecB)`
`vecB = i2piaB`
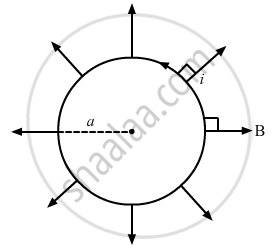
Direction of the force can be found using Fleming's left-hand rule.
Thus, the direction of magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane of the figure and pointing inside.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is it possible for a current loop to stay without rotating in a uniform magnetic field? If yes, what should be the orientation of the loop?
Suppose that the radius of cross-section of the wire used in the previous problem is r. Find the increase in the radius of the loop if the magnetic field is switched off. Young's modulus of the material of the wire is Y.
A 50-turn circular coil of radius 2.0 cm carrying a current of 5.0 A is rotated in a magnetic field of strength 0.20 T. (a) What is the maximum torque that acts on the coil? (b) In a particular position of the coil, the torque acting on it is half of this maximum. What is the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of the coil?
A moving coil galvanometer has been fitted with a rectangular coil having 50 turns and dimensions 5 cm × 3 cm. The radial magnetic field in which the coil is suspended is of 0.05 Wb/m2. The torsional constant of the spring is 1.5 × 10−9 Nm/degree. Obtain the current required to be passed through the galvanometer so as to produce a deflection of 30°.
A Rectangular coil of 10 turns, each of area 0.05 m2, is suspended freely in a uniform magnetic field of induction 0.01 T. A current of 30 µA is passed through it.
(i) What is the magnetic moment of the coil?
(ii) What is the maximum torque experienced by the coil?
Derive an expression for the net torque on a rectangular current carrying loop placed in a uniform magnetic field with its rotational axis perpendicular to the field.
A 100 turn rectangular coil measuring 0.02 m x 0.06 m of an ammeter is in a magnetic field of induction 0.4 tesla. The torsional constant of the suspension fibre is 5 x 10-7 newton x metre/degree. The maximum reading of the ammeter corresponds to a deflection of the coil through 30°. If the magnetic field is radial, then the maximum current that can be measured with this ammeter is ____________.
The `(tau - theta)` graph for a coil is
A small cylindrical soft iron piece is kept in a galvanometer so that
If in a moving coil galvanometer, a current I produces a deflection `theta,` then ____________.
A rectangular coil has 200 turns each of area 50 cm2 . It is capable of rotation about an axis joining the mid points of two opposite sides. When a current of 10 A is passed through it while its plane is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque of 5 Nm. The magnetic field will be ____________.
Two galvanometers 'G1' and 'G2' require 2 mA and 3 mA respectively to produce the same deflection. Then _______.
The current flowing through moving coil galvanometer is 20% of the current to be measured. The resistance of moving coil galvanometer is 48 `Omega`, then shunt required is ____________.
A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the
(a) total torque on the coil,
(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10–5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m–3.)
A current of 10 A is flowing in a wire of length 1.5 m. A force of 15 N acts on it when it is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 2 T. The angle between the magnetic field and the direction of the current is ______.
Equal current i flows in two segments of a circular loop in the direction shown in figure. Radius of the loop is r. The magnitude of magnetic field induction at the centre of the loop is ______.
Calculate the orbital magnetic dipole moment of the electron in the second Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom, given the radius of the orbit is 2.1 Å and the orbital speed is 1.1 × 106 m/s.
A rectangular coil of 10 turns, each of area 0.05 m2, is suspended freely in a radial magnetic field of 0.01 T. If the torsional constant of the suspension fibre is 5 × 10−9 N·m per degree, find the angle through which the coil rotates when a current of 30 μA is passed through it.
A circular coil having N turns of radius R carrying a current I is used to produce a magnetic field B at its centre O.
If this coil is opened and rewound such that the radius of the newly formed coil is 2R, carrying the same current I, what will be the magnetic field at the centre O?
