Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
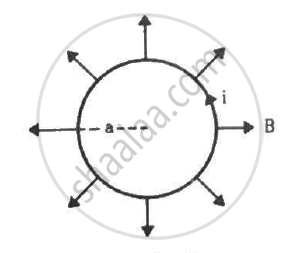
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
Solution
Given:-
A circular loop of radius = a
So, the length of the loop, l = 2πa
Electric current through the loop = i
As per the question,
The loop is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field. The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B
Therefore, the magnetic field points radially outwards.
Here, the angle between the length of the loop and the magnetic field, θ = 90˚
Magnetic force is given by
`|vecF| = iveclxx vecB`
`vecF = i(2piaxxvecB)`
`vecB = i2piaB`
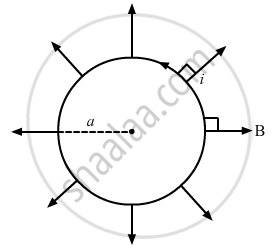
Direction of the force can be found using Fleming's left-hand rule.
Thus, the direction of magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane of the figure and pointing inside.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A circular loop of area 1 cm2, carrying a current of 10 A, is placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The torque on the loop due to the magnetic field is
A rectangular loop of sides 20 cm and 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists parallel to the longer side of the loop. (a) What is the force acting on the loop? (b) What is the torque acting on the loop?
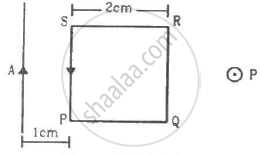
A square loop PQRS carrying a current of 6.0 A is placed near a long wire carrying 10 A as shown in figure. (a) Show that the magnetic force acting on the part PQ is equal and opposite to the part RS. (b) Find the magnetic force on the square loop.
A circular loop of one turn carries a current of 5.00 A. If the magnetic field B at the centre is 0.200 mT, find the radius of the loop.
A current-carrying circular coil of 100 turns and radius 5.0 cm produces a magnetic field of 6.0 × 10−5 T at its centre. Find the value of the current.
Torque acting on a rectangular coil carrying current 'l' situated parallel to magnetic field of induction 'B', having number of turns 'n' and area 'A' is ______.
The `(tau - theta)` graph for a coil is
A triangular loop of side `l` carries a current I. It is placed in a magnetic field B such that the plane of the loop is in the direction of B. The torque on the loop is ____________.
A rectangular coil has 200 turns each of area 50 cm2 . It is capable of rotation about an axis joining the mid points of two opposite sides. When a current of 10 A is passed through it while its plane is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque of 5 Nm. The magnetic field will be ____________.
The sensitivity of a milliammeter of range 0 to 50 mA is x `"div"/"mA"`. If it is converted into an ammeter of range 500 mA by using a suitable shunt then the sensitivity will be ________.
If the net magnetic force acting on a loop is zero then ____________.
What is the magnetic moment of a current-carrying circular coil if the radius of the circular coil is 'R' and magnetic induction at the center is 'B'?
A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the
(a) total torque on the coil,
(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10–5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m–3.)
Two cylinders A and B of the same material have same length, their radii being in the ratio 1 : 2 respectively. The two are joined end to end as shown in the figure. One end of cylinder A is rigidly clamped while free end of cylinder B is twisted through an angle θ. The angle of twist of cylinder A is ______.
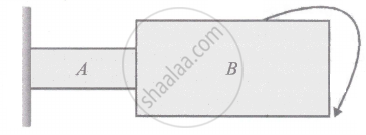
A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed points and carries a current I in the clockwise direction, as shown in the figure. When the system is put in a uniform magnetic field of strength B going into the plane of the paper, the wire takes the shape of a circle. The tension in the wire is ______.
Write the formula for torque acting on rotating current carrying coil in terms of magnetic dipole moment, in vector form.
An electron moving along positive X axis with a velocity of 8 ×107ms-1 enters a region having uniform magnetic field B = 1.3 × 10-3 T along positive Y axis.
- Explain why the electron describes a circular path.
- Calculate the radius of the circular path described by the electron.
