Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A square loop PQRS carrying a current of 6.0 A is placed near a long wire carrying 10 A as shown in figure. (a) Show that the magnetic force acting on the part PQ is equal and opposite to the part RS. (b) Find the magnetic force on the square loop.
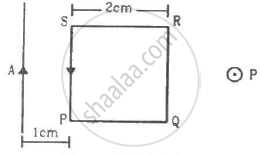
Solution
Given:
Current in the loop, i1 = 6 A
Current in the wire, i2 = 10 A
Now, consider an element on PQ of width dx at a distance x from the wire.
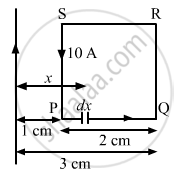
Force on the element is given by
Force acting on part PQ is given by
Both forces are equal in magnitude, but they are opposite in direction.
(b) The magnetic field intensity due to wire on SP is given by
(Towards right)
Force on part RQ is given by
(Towards left)
Thus, the net force on the loop is given by
(Towards right)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of suspended coil type moving coil galvanometer.
Two identical circular loops, P and Q, each of radius r and carrying equal currents are
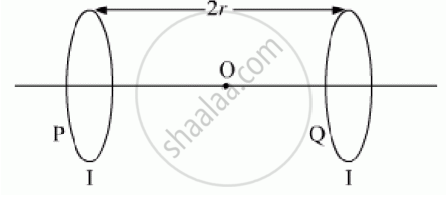
kept in the parallel planes having a common axis passing through O. The direction of current in P is clockwise and in Q is anti-clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from the loops P and Q. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at O.
A circular loop of area 1 cm2, carrying a current of 10 A, is placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The torque on the loop due to the magnetic field is
A current loop of arbitrary shape lies in a uniform magnetic field B. Show that the net magnetic force acting on the loop is zero.
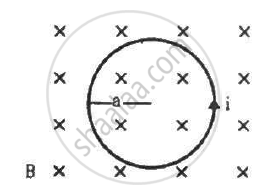
The figure shows a circular wire loop of radius a and carrying a current i, which is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. (a) Consider a small part dl of the wire. Find the force on this part of the wire exerted by the magnetic field. (b) Find the force of compression in the wire.
Derive the expression for the torque acting on a current-carrying loop placed in a magnetic field.
Derive the expression for the torque on a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field.
Torque acting on a rectangular coil carrying current 'l' situated parallel to magnetic field of induction 'B', having number of turns 'n' and area 'A' is ______.
The
Two galvanometers 'G1' and 'G2' require 2 mA and 3 mA respectively to produce the same deflection. Then _______.
If number of turns in moving coil galvanometer becomes half, then the deflection for the same current will become ____________.
The sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer is inversely proportional to ____________.
In suspended type of moving coil galvanometer ____________.
An ammeter is obtained by shunting 'n'
A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the
(a) total torque on the coil,
(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10–5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m–3.)
Two cylinders A and B of the same material have same length, their radii being in the ratio 1 : 2 respectively. The two are joined end to end as shown in the figure. One end of cylinder A is rigidly clamped while free end of cylinder B is twisted through an angle θ. The angle of twist of cylinder A is ______.
When the plane of the coil is parallel to the field, torque will be ______
The initial pressure and volume of a gas enclosed in a cylinder are 2 × 105 N/m2 and 6 × 10-3 m3 respectively. If the work done in compressing the gas at constant pressure is 150 J. find the final volume of the gas.
Write the formula for torque acting on rotating current carrying coil in terms of magnetic dipole moment, in vector form.
