Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two identical circular loops, P and Q, each of radius r and carrying equal currents are
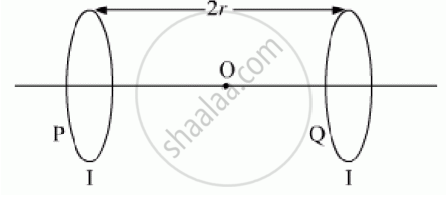
kept in the parallel planes having a common axis passing through O. The direction of current in P is clockwise and in Q is anti-clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from the loops P and Q. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at O.
Solution
The standard formula for field at an axial point is given as
`B=(mu_0ia^2)/(2(a^2 +d^2)^(2/3))`
So, in this case
`B = (mu_0Ir^2)/(2(r^2 +((2r)/2)^2)^(3/2)) = (mu_0I)/((2)^(5/2)r)`
Now, as the current flowing in loop P is clockwise by using right hand thumb’s rule the direction of the magnetic field will be towards left and as the current in loop Q is clockwise then the direction of magnetic field is towards left. So the net magnetic field at point O will be the sum of the magnetic fields due to loops P and Q.
Also, as the fields produced are at an equal distance to O, BP = BQ,
So, net field
`B=B_P+B_Q= 2(mu_0I)/((2)^(5/3)r) = (mu_0I)/((2)^(3/2)r)`
RELATED QUESTIONS
The torque on a current loop is zero if the angle between the positive normal and the magnetic field is either θ = 0 or θ = 180°. In which of the two orientations, the equilibrium is stable?
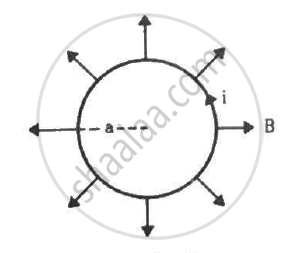
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
A circular loop carrying a current i is made of a wire of length L. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the plane of the loop. (a) Find the torque on the loop. (b) If the same length of the wire is used to form a square loop, what would be the torque? Which is larger?
A 50-turn circular coil of radius 2.0 cm carrying a current of 5.0 A is rotated in a magnetic field of strength 0.20 T. (a) What is the maximum torque that acts on the coil? (b) In a particular position of the coil, the torque acting on it is half of this maximum. What is the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of the coil?
A square loop PQRS carrying a current of 6.0 A is placed near a long wire carrying 10 A as shown in figure. (a) Show that the magnetic force acting on the part PQ is equal and opposite to the part RS. (b) Find the magnetic force on the square loop.
A moving coil galvanometer has been fitted with a rectangular coil having 50 turns and dimensions 5 cm × 3 cm. The radial magnetic field in which the coil is suspended is of 0.05 Wb/m2. The torsional constant of the spring is 1.5 × 10−9 Nm/degree. Obtain the current required to be passed through the galvanometer so as to produce a deflection of 30°.
A triangular loop of side `l` carries a current I. It is placed in a magnetic field B such that the plane of the loop is in the direction of B. The torque on the loop is ____________.
If in a moving coil galvanometer, a current I produces a deflection `theta,` then ____________.
A circular coil having N turns of radius R carrying a current I is used to produce a magnetic field B at its centre O.
If this coil is opened and rewound such that the radius of the newly formed coil is 2R, carrying the same current I, what will be the magnetic field at the centre O?
An electron moving along positive X axis with a velocity of 8 ×107ms-1 enters a region having uniform magnetic field B = 1.3 × 10-3 T along positive Y axis.
- Explain why the electron describes a circular path.
- Calculate the radius of the circular path described by the electron.
