Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
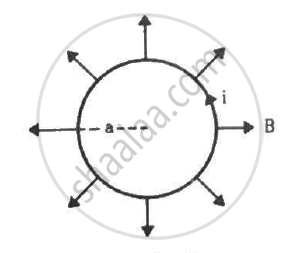
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
उत्तर
Given:-
A circular loop of radius = a
So, the length of the loop, l = 2πa
Electric current through the loop = i
As per the question,
The loop is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field. The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B
Therefore, the magnetic field points radially outwards.
Here, the angle between the length of the loop and the magnetic field, θ = 90˚
Magnetic force is given by
`|vecF| = iveclxx vecB`
`vecF = i(2piaxxvecB)`
`vecB = i2piaB`
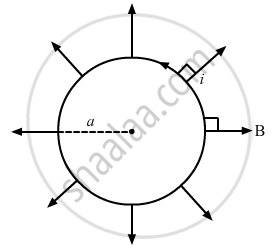
Direction of the force can be found using Fleming's left-hand rule.
Thus, the direction of magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane of the figure and pointing inside.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of suspended coil type moving coil galvanometer.
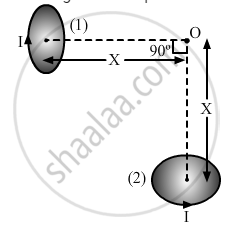
Two very small identical circular loops, (1) and (2), carrying equal currents I are placed vertically (with respect to the plane of the paper) with their geometrical axes perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at the point O.
Two identical circular loops, P and Q, each of radius r and carrying equal currents are
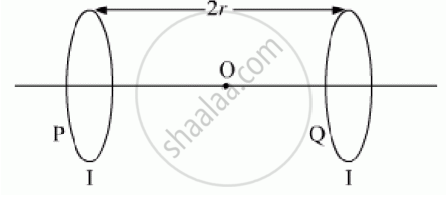
kept in the parallel planes having a common axis passing through O. The direction of current in P is clockwise and in Q is anti-clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from the loops P and Q. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at O.
Will a current loop placed in a magnetic field always experience a zero force?
A rectangular loop of sides 20 cm and 10 cm carries a current of 5.0 A. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.20 T exists parallel to the longer side of the loop. (a) What is the force acting on the loop? (b) What is the torque acting on the loop?
A 50-turn circular coil of radius 2.0 cm carrying a current of 5.0 A is rotated in a magnetic field of strength 0.20 T. (a) What is the maximum torque that acts on the coil? (b) In a particular position of the coil, the torque acting on it is half of this maximum. What is the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of the coil?
A Rectangular coil of 10 turns, each of area 0.05 m2, is suspended freely in a uniform magnetic field of induction 0.01 T. A current of 30 µA is passed through it.
(i) What is the magnetic moment of the coil?
(ii) What is the maximum torque experienced by the coil?
A rectangular coil of length 0.12 m and width 0.1 m having 100 turns of wire is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.4 Wb/m2. The coil carries a current of 2.5 A. If the plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° with the direction of the field, the torque required to keep the coil in stable equilibrium will be ____________.
Torque acting on a rectangular coil carrying current 'l' situated parallel to magnetic field of induction 'B', having number of turns 'n' and area 'A' is ______.
If in a moving coil galvanometer, a current I produces a deflection `theta,` then ____________.
The sensitivity of a milliammeter of range 0 to 50 mA is x `"div"/"mA"`. If it is converted into an ammeter of range 500 mA by using a suitable shunt then the sensitivity will be ________.
If number of turns in moving coil galvanometer becomes half, then the deflection for the same current will become ____________.
The sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer is inversely proportional to ____________.
The magnetic field developed due to current carrying coil at its centre is 'B'. If the new coil of two turns is prepared from the above coil and same current is passed, then the magnetic field at the centre of the new coil will be ____________.
An ammeter is obtained by shunting 'n' `Omega` galvanometer with 'n' `Omega` resistance. The additional shunt required to be connected across it to double the range is ____________.
What is the magnetic moment of a current-carrying circular coil if the radius of the circular coil is 'R' and magnetic induction at the center is 'B'?
Two cylinders A and B of the same material have same length, their radii being in the ratio 1 : 2 respectively. The two are joined end to end as shown in the figure. One end of cylinder A is rigidly clamped while free end of cylinder B is twisted through an angle θ. The angle of twist of cylinder A is ______.
When the plane of the coil is parallel to the field, torque will be ______
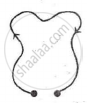
A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed points and carries a current I in the clockwise direction, as shown in the figure. When the system is put in a uniform magnetic field of strength B going into the plane of the paper, the wire takes the shape of a circle. The tension in the wire is ______.
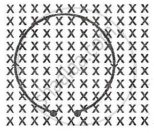
Calculate the orbital magnetic dipole moment of the electron in the second Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom, given the radius of the orbit is 2.1 Å and the orbital speed is 1.1 × 106 m/s.
