Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A cyclist is travelling at 15 m s-1. She applies brakes so that she does not collide with a wall 18 m away. What deceleration must she have ?
उत्तर
We have to find the deceleration. We have the following information given,
Initial velocity, (u) = 15 m/s
Final velocity, (v) = 0 m/s
Distance travelled, (s) = 18 m
Let the acceleration be (a)
We can calculate acceleration by using the 3rd equation of motion,
`a = (v^2 - u^2)/(2s)`
Put the values in above equation to find the deceleration,
a = (0-225)/(36)
⇒ `a =-6.25 "m/s"^2`
Thus , the deceleration is 6.25 `"m/s"^2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following case:
A car moving with a constant speed.
Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following case:
A car parked on a side road.
Figure shows the distance-time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?
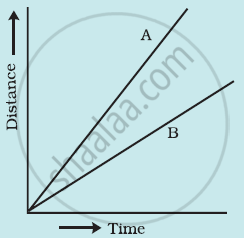
Figure: Distance-time graph for the motion of two cars
Name the two quantities, the slope of whose graph give speed .
The graph given alongside shows the positions of a body at different times. Calculate the speed of the body as it moves from :
(1) A to B,
(2) B to C, and
(3) C to D.

A car is travelling at 20 m/s along a road. A child runs out into the road 50 m ahead and the car driver steps on the brake pedal. What must the car’s deceleration be if the car is to stop just before it reaches the child ?
Two friends leave Delhi for Chandigarh in their cars. A starts at 5 am and moves with a constant speed of 30 km/h, whereas B starts at 6 am and moves with a constant speed of 40 kmh-1. Plot the distance-time graph for their motion and find at what time the two friends will meet and at what distance from Delhi.
A body moves along a straight road with a speed of 20 m/s and has a uniform acceleration of 5 m/s2. What will be its speed after 2 s?
Complete the data of the table given below with the help of the distance-time graph given in Figure 13.6
| Distance (m) | 0 | 4 | ? | 12 | ? | 20 |
| Time (s) | 0 | 2 | 4 | ? | 8 | 10 |

