Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
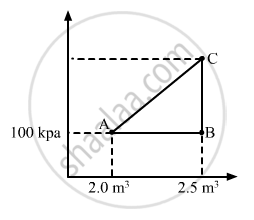
A gas is initially at a pressure of 100 kPa and its volume is 2.0 m3. Its pressure is kept constant and the volume is changed from 2.0 m3 to 2.5 m3. Its Volume is now kept constant and the pressure is increased from 100 kPa to 200 kPa. The gas is brought back to its initial state, the pressure varying linearly with its volume. (a) Whether the heat is supplied to or extracted from the gas in the complete cycle? (b) How much heat was supplied or extracted?
उत्तर
(a) Given:-
P1 = 100 kPa,
V1 = 2 m3
V2 = 2.5 m3
∆V = 0.5 m3
Work done, W = P∆V
\[W = 100 \times {10}^3 \times 0 . 5\]
\[W = 5 \times {10}^4 J\]
WAB = Area under line AB = 5 × 104 J
If volume is kept constant for line BC, then ∆V = 0.
WBC = P∆V = 0
Work done while going from point B to C = 0
When the system comes back to the initial point A from C, work done is equal to area under line AC.
WCA = Area of triangle ABC + Area of rectangle under line AB
Total work done, W = Area enclosed by the ABCA
W = WAC - WAB
From the graph, we see that the area under AC is greater than the area under AB. We also see that heat is extracted from the system as change in the internal energy is zero.
(b) Amount of heat extracted = Area enclosed under ABCA
\[= \frac{1}{2} \times 0 . 5 \times 100 \times {10}^3 = 25000 J\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2, if brought in thermal contact, do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2)/2.
Explain why Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
Do the intermediate states of the system (before settling to the final equilibrium state) lie on its P-V-T surface?
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the changes in internal energy of the system in the process A and B. Then _____________ .

Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
What is the internal energy of the system, when the amount of heat Q is added to the system and the system does not do any work during the process?
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam at a pressure of 1 atm. The latent heat of vaporization at this pressure is 2256 J/g. Calculate the external work and the increase in internal energy.
A cylinder containing one gram molecule of the gas was compressed adiabatically until its temperature rose from 27°C to 97°C. Calculate the work done and heat produced in the gas (𝛾 = 1.5).
The internal energy of a system is ______
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
n mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes:
A `→` B: Isothermal expansion at temperature T so that the volume is doubled from V1 to V2 = 2V1 and pressure changes from P1 to P2.
B `→` C: Isobaric compression at pressure P2 to initial volume V1.
C `→` A: Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from P2 to P1.
Total workdone in the complete cycle ABCA is ______.

An expansion process on a diatomic ideal gas (Cv = 5/2 R), has a linear path between the initial and final coordinates on a pV diagram. The coordinates of the initial state are: the pressure is 300 kPa, the volume is 0.08 m3 and the temperature is 390 K. The final pressure is 90 kPa and the final temperature s 320 K. The change in the internal energy of the gas, in SI units, is closest to:
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50 N/m2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is ______.
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The internal energy of one mole of argon at 300 K is ______. (R = 8.314 J/mol.K)
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
