Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the internal energy of the system, when the amount of heat Q is added to the system and the system does not do any work during the process?
उत्तर
The first law of thermodynamics is one of the most useful equations when dealing with internal energy, and it states that the change in internal energy of a system equals the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system.
∆U = Q − W
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
A closed bottle contains some liquid. the bottle is shaken vigorously for 5 minutes. It is found that the temperature of the liquid is increased. Is heat transferred to the liquid? Is work done on the liquid? Neglect expansion on heating.
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
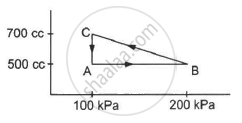
A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J ?
Which of the following system freely allows the exchange of energy and matter with its environment?
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
The internal energy of a system is ______
An ideal gas is compressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy will ____________.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in the temperature of the gas?
n mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes:
A `→` B: Isothermal expansion at temperature T so that the volume is doubled from V1 to V2 = 2V1 and pressure changes from P1 to P2.
B `→` C: Isobaric compression at pressure P2 to initial volume V1.
C `→` A: Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from P2 to P1.
Total workdone in the complete cycle ABCA is ______.

An expansion process on a diatomic ideal gas (Cv = 5/2 R), has a linear path between the initial and final coordinates on a pV diagram. The coordinates of the initial state are: the pressure is 300 kPa, the volume is 0.08 m3 and the temperature is 390 K. The final pressure is 90 kPa and the final temperature s 320 K. The change in the internal energy of the gas, in SI units, is closest to:
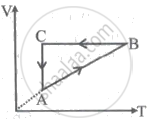
A cyclic process ABCA is shown in the V-T diagram. A process on the P-V diagram is ______.
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The internal energy of one mole of argon at 300 K is ______. (R = 8.314 J/mol.K)
The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
What is heat?
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
