Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
उत्तर
Internal energy of a system increases if its temperature increases. This is valid only for the system of ideal gases and not for all the systems.
For example:- During meting process, temperature of the system remains constant, but internal energy change increases by mL.
⇒ ΔU = mL
Here,
m = Mass of the solid
L = Latent heat of the solid
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The outer surface of a cylinder containing a gas is rubbed vigorously by a polishing machine. The cylinder and its gas become warm. Is the energy transferred to the gas heat or work?
Consider the process on a system shown in figure. During the process, the work done by the system ______________ .
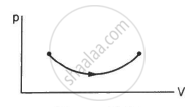
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure.
The volumes in the initial states are the same in the two processes and the volumes in the final states are also the same. Let ∆W1 and ∆W2 be the work done by the system in the processes A and B respectively.
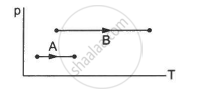
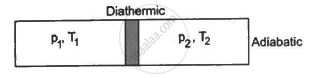
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of volume V with adiabatic walls containing an ideal gas. The internal energy of this ideal gas is given by 1.5 nRT. The tube is divided into two equal parts by a fixed diathermic wall. Initially, the pressure and the temperature are p1, T1 on the left and p2, T2 on the right. The system is left for sufficient time so that the temperature becomes equal on the two sides. (a) How much work has been done by the gas on the left part? (b) Find the final pressures on the two sides. (c) Find the final equilibrium temperature. (d) How much heat has flown from the gas on the right to the gas on the left?
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam at a pressure of 1 atm. The latent heat of vaporization at this pressure is 2256 J/g. Calculate the external work and the increase in internal energy.
A cylinder containing one gram molecule of the gas was compressed adiabatically until its temperature rose from 27°C to 97°C. Calculate the work done and heat produced in the gas (𝛾 = 1.5).
derive the relation between the change in internal energy (∆U), work is done (W), and heat (Q).
The internal energy of a system is ______
A thermodynamic system goes from states
(i) P, V to 2P, V (ii) P, V to P, 2V
The work done in the two cases is ____________.
Two samples A and B, of a gas at the same initial temperature and pressure are compressed from volume V to V/2; A isothermally and B adiabatically. The final pressure of A will be ______.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
Figure shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.

- Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
- Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
- Work done is maximum in case I
- Work done is minimum in case II.
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50 N/m2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is ______.
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
What is heat?
