Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
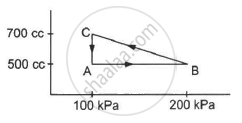
A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J ?
उत्तर
Heat given in the process, ∆Q = 2.4 cal
∆W = WAB + WBC + WCA
For line AB:-
Change in volume,
ΔV = 0
∴ WAB = 0
For line BC :-
Mean pressure, \[P = \frac{1}{2} \times (100 + 200) kPa = 150 \times {10}^3 Pa\]
\[ ∆ V = (700 - 500) cc = 200 cc\]
\[ W_{BC} = 150 \times {10}^3 \times 200 \times {10}^{- 6} \]
\[ W_{BC} = 30 J\]
For line AC :-
P = 100 kPa
ΔV = 200 cc
WCA = 100 × 103 × 200 × 10−6
Total work done in the one cycle is given by
∆W = 0 + 150× 103 × 200 × 10−6 − 100 × 103 × 200 × 10−6
∆W = `1/2` × 300 × 103 × 200 × 10−6 − 20
∆W = 30 J − 20 J = 10 J
∆U = 0 .............(in a cyclic process)
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
⇒ 2.4J = 10
\[\Rightarrow J = \frac{10}{2 . 4} = \frac{100}{24} = \frac{25}{6} = 4 . 17 \text{J/cal}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
Do the intermediate states of the system (before settling to the final equilibrium state) lie on its P-V-T surface?
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston. The piston is suddenly moved in to compress the gas and is maintained at this position. As time passes the pressure of the gas in the cylinder ______________ .
In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to the final pressure and volume.
(a) The initial temperature must be equal to the final temperature.
(b) The initial internal energy must be equal to the final internal energy.
(c) The net heat given to the system in the process must be zero.
(d) The net work done by the system in the process must be zero.
A gas is initially at a pressure of 100 kPa and its volume is 2.0 m3. Its pressure is kept constant and the volume is changed from 2.0 m3 to 2.5 m3. Its Volume is now kept constant and the pressure is increased from 100 kPa to 200 kPa. The gas is brought back to its initial state, the pressure varying linearly with its volume. (a) Whether the heat is supplied to or extracted from the gas in the complete cycle? (b) How much heat was supplied or extracted?
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
When does a system lose energy to its surroundings and its internal energy decreases?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Explain given cases related to energy transfer between the system and surrounding –
- energy transferred (Q) > 0
- energy transferred (Q) < 0
- energy transferred (Q) = 0
Explain the different ways through which the internal energy of the system can be changed.
The internal energy of a system is ______
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
A cyclic process ABCA is shown in the V-T diagram. A process on the P-V diagram is ______.
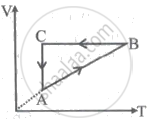
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
