Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
विकल्प
System gains energy
System loses energy
System releases energy
the system does not exchange energy
उत्तर
System gains energy
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2, if brought in thermal contact, do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2)/2.
Explain why Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
A cylinder containing a gas is lifted from the first floor to the second floor. What is the amount of work done on the gas? What is the amount of work done by the gas? Is the internal energy of the gas increased? Is the temperature of the gas increased?
An ideal gas is pumped into a rigid container having diathermic walls so that the temperature remains constant. In a certain time interval, the pressure in the container is doubled. Is the internal energy of the contents of the container also doubled in the interval ?
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
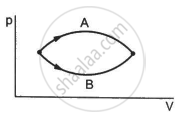
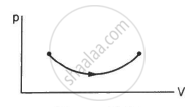
Consider the process on a system shown in figure. During the process, the work done by the system ______________ .
An ideal gas goes from the state i to the state f as shown in figure. The work done by the gas during the process ______________ .
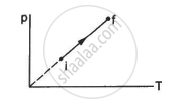
Figure shows three paths through which a gas can be taken from the state A to the state B. Calculate the work done by the gas in each of the three paths.
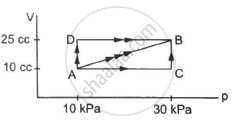
A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J ?
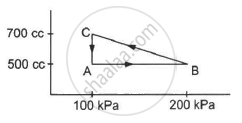
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
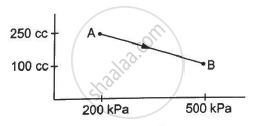
A gas is initially at a pressure of 100 kPa and its volume is 2.0 m3. Its pressure is kept constant and the volume is changed from 2.0 m3 to 2.5 m3. Its Volume is now kept constant and the pressure is increased from 100 kPa to 200 kPa. The gas is brought back to its initial state, the pressure varying linearly with its volume. (a) Whether the heat is supplied to or extracted from the gas in the complete cycle? (b) How much heat was supplied or extracted?
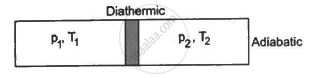
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of volume V with adiabatic walls containing an ideal gas. The internal energy of this ideal gas is given by 1.5 nRT. The tube is divided into two equal parts by a fixed diathermic wall. Initially, the pressure and the temperature are p1, T1 on the left and p2, T2 on the right. The system is left for sufficient time so that the temperature becomes equal on the two sides. (a) How much work has been done by the gas on the left part? (b) Find the final pressures on the two sides. (c) Find the final equilibrium temperature. (d) How much heat has flown from the gas on the right to the gas on the left?
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
What is the internal energy of the system, when the amount of heat Q is added to the system and the system does not do any work during the process?
Explain the different ways through which the internal energy of the system can be changed.
derive the relation between the change in internal energy (∆U), work is done (W), and heat (Q).
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in the temperature of the gas?
In insulated systems, the amount of external work done by the gas is proportional to:
Figure shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.

- Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
- Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
- Work done is maximum in case I
- Work done is minimum in case II.
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
An expansion process on a diatomic ideal gas (Cv = 5/2 R), has a linear path between the initial and final coordinates on a pV diagram. The coordinates of the initial state are: the pressure is 300 kPa, the volume is 0.08 m3 and the temperature is 390 K. The final pressure is 90 kPa and the final temperature s 320 K. The change in the internal energy of the gas, in SI units, is closest to:
The internal energy of one mole of argon is ______.
The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
