Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
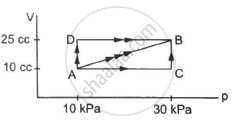
Figure shows three paths through which a gas can be taken from the state A to the state B. Calculate the work done by the gas in each of the three paths.
उत्तर
Work done during any process, W = P ∆ V
If both pressure and volume are changing during a process, then work done can be found out by finding the area under the PV diagram.
In path ACB, for line AC :-
Since initial volume is equal to final volume,
∆ V = 0
⇒ WAC = P ∆ V = 0
For line BC :-
P = 30 × 103 pa
WACB = WAC + WBC = 0 + P∆V
= 30 × 103 × (25 − 10) × 10−6
= 0.45 J
For path AB:-
Since both pressure and volume are changing, we use the mean pressure to find the work done.
Mean pressure, P = \[\frac{1}{2} \times (30 + 10) \times {10}^3\]
WAB = \[\frac{1}{2}\]× (10 + 30) × 103 × 15 × 10−6
= \[\frac{1}{2}\] × 40 × 15 × 10−3 = 0.30 J
Initial volume in path ADB, along line DB is the same as final volume. Thus, work done along this line is zero.
Along line AD, P = 10 kPa
W = WAD + WDB
= 10 × 103 (25 − 10) × 10−6 + 0
= 10 × 15 × 10−3 = 0.15 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state A to another equilibrium state B, an amount of work equal to 22.3 J is done on the system. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, how much is the net work done by the system in the latter case? (Take 1 cal = 4.19 J)
A steam engine delivers 5.4×108 J of work per minute and services 3.6 × 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the efficiency of the engine? How much heat is wasted per minute?
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
Can work be done by a system without changing its volume?
An ideal gas is pumped into a rigid container having diathermic walls so that the temperature remains constant. In a certain time interval, the pressure in the container is doubled. Is the internal energy of the contents of the container also doubled in the interval ?
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
Explain given cases related to energy transfer between the system and surrounding –
- energy transferred (Q) > 0
- energy transferred (Q) < 0
- energy transferred (Q) = 0
A thermodynamic system goes from states
(i) P, V to 2P, V (ii) P, V to P, 2V
The work done in the two cases is ____________.
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
Figure shows the P-V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different parts I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to the same change of state.

- Change in internal energy is same in IV and III cases, but not in I and II.
- Change in internal energy is same in all the four cases.
- Work done is maximum in case I
- Work done is minimum in case II.
n mole of a perfect gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCA (see figure) consisting of the following processes:
A `→` B: Isothermal expansion at temperature T so that the volume is doubled from V1 to V2 = 2V1 and pressure changes from P1 to P2.
B `→` C: Isobaric compression at pressure P2 to initial volume V1.
C `→` A: Isochoric change leading to change of pressure from P2 to P1.
Total workdone in the complete cycle ABCA is ______.

The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
What is heat?
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
