Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
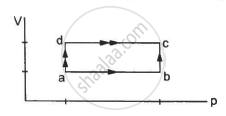
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
उत्तर
Initial point is a and the final point is c.
As internal energy is a state function so it depends only on the initial and final points and not on the path followed by the system. This implies that change in internal energy for path abc and path adc is the same.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
Here, ∆Q is the amount of heat absorbed and ∆U is the change in internal energy of the system. Also, ∆W is the work done by the system.
For path abc:-
∆Q = 80 J, ∆W = 30 J
∆U = (80 − 30) J = 50 J
For path abc:-
∆U =50 J ..............(same as for path abc)
∆W = 10 J
∴ ∆Q = 10 J + 50 J = 60 J ..........(∆U = 50 J)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If the system performs work at a rate of 75 Joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
The internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system.
(a) The process must be adiabatic.
b) The process must be isothermal.
(c) The process must be isobaric.
(d) The temperature must decrease.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
10 kg of four different gases (Cl2, CH4, O2, N2) expand isothermally and reversibly from 20 atm to 10 atm. The order of amount of work will be ____________.
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
A gas performs 0.320 kJ work on surrounding and absorbs 120 J of heat from the surrounding. Hence, change in internal energy is ______.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
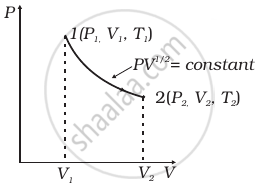
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
An electric appliance supplies 6000 J/min heat to the system. If the system delivers a power of 90 W. How long it would take to increase the internal energy by 2.5 × 103 J?
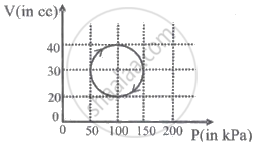
A system is taken through a cyclic process represented by a circle as shown. The heat absorbed by the system is ______.
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
What work will be done, when 3 moles of an ideal gas are compressed to half the initial volume at a constant temperature of 300 K?
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
A monoatomic gas at 27°C is adiabatically compressed to 80% of its initial volume. Find the final temperature of the gas.
Obtain an expression for the workdone by a gas in an isothermal process.
