Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
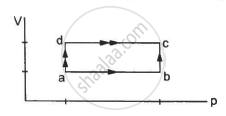
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

उत्तर
Given:-
In path ACB,
∆Q = 50 cal = (50 × 4.2) J
∆Q = 210 J
∆W = WAC + WCB
Since initial and final volumes are the same along the line BC, change in volume of the system along BC is zero.
Hence, work done along this line will be zero.
For line AC:-
P = 50 kPa
Volume changes from 200 cc to 400 cc.
`rArrDelta V =400-200c c=200 c c`
∆W = WAC + WCB
= 50 × 10−3 × 200 × 10−6 + 0
= 10 J
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
⇒ ∆U = ∆Q − ∆W = (210 − 10) J
∆U = 200 J
In path ADB, ∆Q = ?
∆U = 200 J ..............(Internal energy depends only on the initial and final points and not on the path followed.)
⇒ ∆W = WAD + WDB = ∆W
Work done for line AD will also be zero.
For line DB:-
P = 155 kPa
`rArrDelta V =400-200c c=200 c c`
W = 0 + 155 × 103 × 200 × 10−6
W = 31 J
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
∆Q= (200 + 31) J = 231 J
∆Q = 55 cal
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
The internal energy of a gas is given by U = 1.5 pV. It expands from 100 cm3 to 200 cm3against a constant pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas in the process.
A solar cooker and a pressure cooker both are used to cook food. Treating them as thermodynamic systems, discuss the similarities and differences between them.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
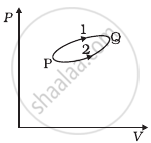
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
Which among the following equations represents the first law of thermodynamics under isobaric conditions?
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
The amount of work done in increasing the voltage across the plates of capacitor from 5 V to 10 V is W. The work done in increasing it from 10 V to 15 V will be ______.
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Show that the heat absorbed at constant pressure is equal to the change in enthalpy of the system.
Obtain an expression for the workdone by a gas in an isothermal process.
Define the isothermal process.
