Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
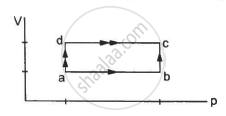
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
उत्तर
Initial point is a and the final point is c.
As internal energy is a state function so it depends only on the initial and final points and not on the path followed by the system. This implies that change in internal energy for path abc and path adc is the same.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
Here, ∆Q is the amount of heat absorbed and ∆U is the change in internal energy of the system. Also, ∆W is the work done by the system.
For path abc:-
∆Q = 80 J, ∆W = 30 J
∆U = (80 − 30) J = 50 J
For path abc:-
∆U =50 J ..............(same as for path abc)
∆W = 10 J
∴ ∆Q = 10 J + 50 J = 60 J ..........(∆U = 50 J)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for Isothermal Process
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
The internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system.
(a) The process must be adiabatic.
b) The process must be isothermal.
(c) The process must be isobaric.
(d) The temperature must decrease.
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
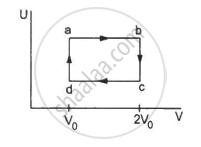
Figure shows the variation in the internal energy U with the volume V of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas in a cyclic process abcda. The temperatures of the gas at b and c are 500 K and 300 K respectively. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas during the process.
An adiabatic vessel of total volume V is divided into two equal parts by a conducting separator. The separator is fixed in this position. The part on the left contains one mole of an ideal gas (U = 1.5 nRT) and the part on the right contains two moles of the same gas. Initially, the pressure on each side is p. The system is left for sufficient time so that a steady state is reached. Find (a) the work done by the gas in the left part during the process, (b) the temperature on the two sides in the beginning, (c) the final common temperature reached by the gases, (d) the heat given to the gas in the right part and (e) the increase in the internal energy of the gas in the left part.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
For an Isothermal process
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
120 J of heat is added to a gaseous system, whose internal energy change is 60 J, then the amount of external work done is ____________.
Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is ______.
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
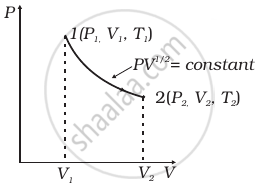
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of ______.
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Adiabatic process
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
Define the isothermal process.
