Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
उत्तर
Given:-
The system comprises of an insulated copper vessel that contains water.
t1 = 15°C, t2 = 17°C
t1 is the initial temperature of the system
t2 is the final temperature of the system
∆t = Change in the temperature of the system= t2 − t1
= 17°C − 15°C = 2°C = 275 K
Mass of the vessel, mv = 100 g = 0.1 kg
Mass of water, mw = 200 g = 0.2 kg
Specific heat capacity of copper, cu = 420 J/kg-K
Specific heat capacity of water, cw = 4200 J/kg-K
(a) Since the system is insulated from the surroundings, no heat is transferred between the system and the surroundings. This implies that the heat transferred to the liquid vessel system is zero. The internal heat is shared between the vessel and water.
(b) Work done on the system
\[= m_w c_w ∆ t + m_v c_u ∆ t\]
⇒ dW = 100 × 10−3 × 420 × 2 + 200 × 10−3 × 4200 × 2
⇒ dW = 84 + 84 × 20 = 84 × 21
⇒ dW = 1764 J
(c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
\[dQ = dW + dU\]
Here, \[dW = pdV\]
Work is done by the system. Thus, work done is negative.
⇒ dQ = 0 .............(given)
dU = − dW
= -(-1764) = 1764 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
10 kg of four different gases (Cl2, CH4, O2, N2) expand isothermally and reversibly from 20 atm to 10 atm. The order of amount of work will be ____________.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
"The mass and energy both are conserved in an isolated system", is the statement of ______.
A gas performs 0.320 kJ work on surrounding and absorbs 120 J of heat from the surrounding. Hence, change in internal energy is ______.
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
Change in internal energy, when 4 KJ of work is done on the system and 1 KJ heat is given out by the system, is:
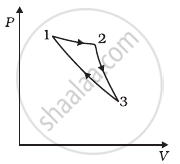
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
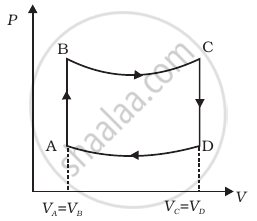
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
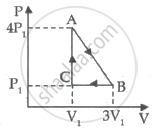
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
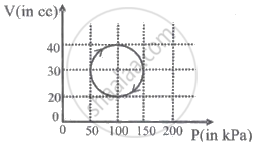
A system is taken through a cyclic process represented by a circle as shown. The heat absorbed by the system is ______.
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
In an adiabatic process, ______.
If the adiabatic ratio for a gas is 5/3, find the molar specific heat capacity of the gas at (i) constant volume (ii) constant pressure.
In an adiabatic expansion of 2 moles of a gas, the initial pressure was 1.013 × 105 Pa, the initial volume was 22.4 L, the final pressure was 3.191 × 104 Pa and the final volume was 44.8 L. Find the work done by the gas on its surroundings. Taken `γ = 5/3`.
