Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
उत्तर
Given:-
The system comprises of an insulated copper vessel that contains water.
t1 = 15°C, t2 = 17°C
t1 is the initial temperature of the system
t2 is the final temperature of the system
∆t = Change in the temperature of the system= t2 − t1
= 17°C − 15°C = 2°C = 275 K
Mass of the vessel, mv = 100 g = 0.1 kg
Mass of water, mw = 200 g = 0.2 kg
Specific heat capacity of copper, cu = 420 J/kg-K
Specific heat capacity of water, cw = 4200 J/kg-K
(a) Since the system is insulated from the surroundings, no heat is transferred between the system and the surroundings. This implies that the heat transferred to the liquid vessel system is zero. The internal heat is shared between the vessel and water.
(b) Work done on the system
\[= m_w c_w ∆ t + m_v c_u ∆ t\]
⇒ dW = 100 × 10−3 × 420 × 2 + 200 × 10−3 × 4200 × 2
⇒ dW = 84 + 84 × 20 = 84 × 21
⇒ dW = 1764 J
(c) Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
\[dQ = dW + dU\]
Here, \[dW = pdV\]
Work is done by the system. Thus, work done is negative.
⇒ dQ = 0 .............(given)
dU = − dW
= -(-1764) = 1764 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
Find the change in the internal energy of 2 kg of water as it is heated from 0°C to 4°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg−1 K−1 and its densities at 0°C and 4°C are 999.9 kg m−3 and 1000 kg m−3 respectively. Atmospheric pressure = 105 Pa.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
The isothermal bulk modulus of a perfect gas at pressure P is numerically equal to ____________.
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
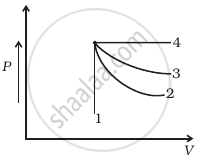
An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram (figure). The amount of work done by the gas is ______.

Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
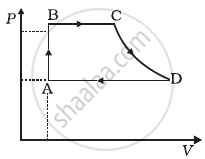
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
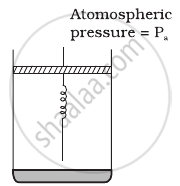
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
In an adiabatic process, ______.
What is true for an adiabatic process?
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
A monoatomic gas at 27°C is adiabatically compressed to 80% of its initial volume. Find the final temperature of the gas.
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Write a short note on isobar.
