Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
विकल्प
conservation of heat
conservation of work
conservation of momentum
conservation of energy
उत्तर
conservation of energy
Heat is a form of energy. Since the first law of thermodynamics deals with the conservation of heat, it actually refers to the conservation of energy in the broader sense.
The first law of thermodynamics is just the restatement of the law of conservation of energy. We observe that the energy supplied to a system will contribute to change in its internal energy and the amount of work done by the system on its surroundings.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
The internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system.
(a) The process must be adiabatic.
b) The process must be isothermal.
(c) The process must be isobaric.
(d) The temperature must decrease.
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

Find the change in the internal energy of 2 kg of water as it is heated from 0°C to 4°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg−1 K−1 and its densities at 0°C and 4°C are 999.9 kg m−3 and 1000 kg m−3 respectively. Atmospheric pressure = 105 Pa.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
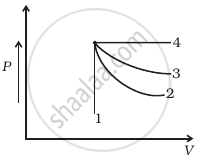
Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is ______.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
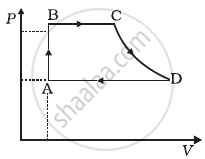
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
A system is taken through a cyclic process represented by a circle as shown. The heat absorbed by the system is ______.
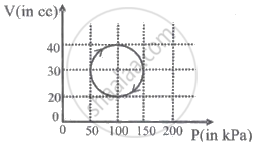
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
The amount of work done in increasing the voltage across the plates of capacitor from 5 V to 10 V is W. The work done in increasing it from 10 V to 15 V will be ______.
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
