Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
उत्तर
According to the first law of thermodynamics, “the total energy of a system and surroundings remains constant when the system changes from an initial state to final state.”
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If the system performs work at a rate of 75 Joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this process? Is heat given to the object equal to the increase in its internal energy?
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
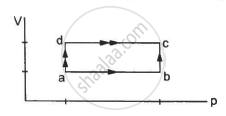
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

The internal energy of a gas is given by U = 1.5 pV. It expands from 100 cm3 to 200 cm3against a constant pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas in the process.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA, shown in figure, performed on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas. A total of 1200 J of heat is withdrawn from the sample in the process. Find the work done by the gas during the part BC.
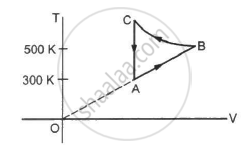
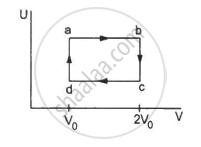
Figure shows the variation in the internal energy U with the volume V of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas in a cyclic process abcda. The temperatures of the gas at b and c are 500 K and 300 K respectively. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas during the process.
For an Isochoric process
Define an isolated system.
10 kg of four different gases (Cl2, CH4, O2, N2) expand isothermally and reversibly from 20 atm to 10 atm. The order of amount of work will be ____________.
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
A gas performs 0.320 kJ work on surrounding and absorbs 120 J of heat from the surrounding. Hence, change in internal energy is ______.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram (figure). The amount of work done by the gas is ______.

Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
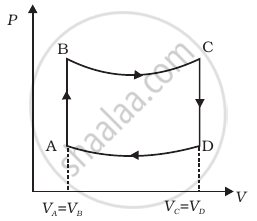
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
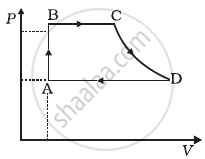
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
In the reported figure, heat energy absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process is ______ πJ.
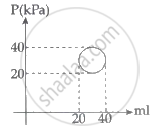
An electric appliance supplies 6000 J/min heat to the system. If the system delivers a power of 90 W. How long it would take to increase the internal energy by 2.5 × 103 J?
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
Mathematical equation of first law of thermodynamics for isochoric process is ______.
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
One mole of an ideal gas is allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from a temperature of 27°C. If the work done during the process is 3 kJ, the final temperature will be equal to ______.
(Cv = 20 JK−1)
Which among the following equations represents the first law of thermodynamics under isobaric conditions?
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
A given system undergoes a change in which the work done by the system equals the decrease in its internal energy. The system must have undergone an ______.
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
What is true for an adiabatic process?
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
In an adiabatic expansion of 2 moles of a gas, the initial pressure was 1.013 × 105 Pa, the initial volume was 22.4 L, the final pressure was 3.191 × 104 Pa and the final volume was 44.8 L. Find the work done by the gas on its surroundings. Taken `γ = 5/3`.
What is Isobaric process?
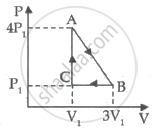
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
Define isochoric process
What is an isothermal process?
