Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The pressure of a gas changes linearly with volume from 10 kPa, 200 cc to 50 kPa, 50 cc. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) If no heat is supplied or extracted from the gas, what is the change in the internal energy of the gas?
उत्तर
Initial pressure of the system, P1 = 10 kPa = 10 × 103 Pa
Final pressure of the system, P2 = 50 kPa = 50 × 103 Pa
Initial volume of the system, V1 = 200 cc
Final volume of the system, V2 = 50 cc
(i) Work done on the gas = Pressure × Change in volume of the system
Since pressure is also changing, we take the average of the given two pressures.
Now,
\[P=\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)\left( 10 + 50 \right) \times {10}^3\]
\[=30 \times {10}^3\]Pa
Work done by the system of gas can be given by
\[30 \times {10}^3 \times \left( 50 - 200 \right) \times {10}^{- 6} \]
\[ = - 4 . 5 J\]
(ii) Since no heat is supplied to the system, ∆Q = 0.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
∆U = − ∆W = 4.5 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If the system performs work at a rate of 75 Joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Calculate the increase in the internal energy of 10 g of water when it is heated from 0°C to 100°C and converted into steam at 100 kPa. The density of steam = 0.6 kg m−3. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and the latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.25 × 10 6J kg−1.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
The isothermal bulk modulus of a perfect gas at pressure P is numerically equal to ____________.
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
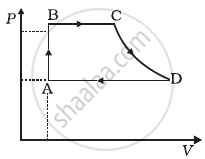
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Mathematical equation of first law of thermodynamics for isochoric process is ______.
Which among the following equations represents the first law of thermodynamics under isobaric conditions?
The V cc volume of gas having `γ = 5/2` is suddenly compressed to `(V/4)` cc. The initial pressure of the gas is p. The final pressure of the gas will be ______.
What work will be done, when 3 moles of an ideal gas are compressed to half the initial volume at a constant temperature of 300 K?
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
Explain the formulation of first law of thrmodynamics.
Write a short note on isobar.
