Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
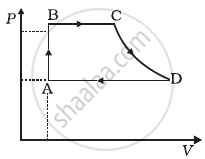
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
उत्तर
a. By using the first law of thermodynamics, we can find the amount of heat associated with each process
For process AB
Volume is constant, hence work done dW = 0
According to first law of thermodynamics,
=
=
=
=
=
b. For process BC, P = constant
=
=
=
Heat exchanged =
c. For process CD, QCD = 0 .....(As the change is adiabatic.)
d. In process DA involves compression of gas from VD to VA at constant pressure PA.
∴ Heat exchanged can be calculated in a similar way as process BC.
Hence,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
Define an isolated system.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
The compressibility of water is 5 × 10-10 m2/N. Pressure of 15 × 106 Pa is applied on 100 ml volume of water. The change in the volume of water is ______.
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
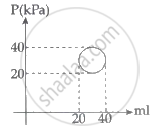
In the reported figure, heat energy absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process is ______ πJ.
If the adiabatic ratio for a gas is 5/3, find the molar specific heat capacity of the gas at (i) constant volume (ii) constant pressure.
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
