Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
उत्तर
The internal energy of a system is the sum of the potential and kinetic energy of all the system's constituents. In the preceding example, the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy is responsible for the significant increase in pressure and temperature of the hydrogen and oxygen mixture ignited by the spark.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
A thermally insulated, closed copper vessel contains water at 15°C. When the vessel is shaken vigorously for 15 minutes, the temperature rises to 17°C. The mass of the vessel is 100 g and that of the water is 200 g. The specific heat capacities of copper and water are 420 J kg−1 K−1 and 4200 J kg−1 K−1 respectively. Neglect any thermal expansion. (a) How much heat is transferred to the liquid-vessel system? (b) How much work has been done on this system? (c) How much is the increase in internal energy of the system?
The internal energy of a gas is given by U = 1.5 pV. It expands from 100 cm3 to 200 cm3against a constant pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas in the process.
A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is slowly heated for some time. During the process, 10 J of heat is supplied and the piston is found to move out 10 cm. Find the increase in the internal energy of the gas. The area of cross section of the cylinder = 4 cm2 and the atmospheric pressure = 100 kPa.
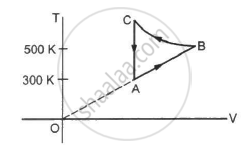
Consider the cyclic process ABCA, shown in figure, performed on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas. A total of 1200 J of heat is withdrawn from the sample in the process. Find the work done by the gas during the part BC.
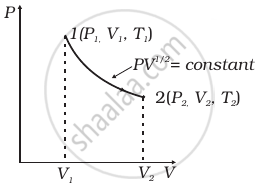
Calculate the increase in the internal energy of 10 g of water when it is heated from 0°C to 100°C and converted into steam at 100 kPa. The density of steam = 0.6 kg m−3. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and the latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.25 × 10 6J kg−1.
For an Isothermal process
10 kg of four different gases (Cl2, CH4, O2, N2) expand isothermally and reversibly from 20 atm to 10 atm. The order of amount of work will be ____________.
When heat energy of 2000 joules is supplied to a gas at constant pressure 2.1 x 105 N/m2, there is an increase in its volume equal to 2.5 x 10-3 m3. The increase in internal energy of the gas in joules is ____________.
A gas performs 0.320 kJ work on surrounding and absorbs 120 J of heat from the surrounding. Hence, change in internal energy is ______.
120 J of heat is added to a gaseous system, whose internal energy change is 60 J, then the amount of external work done is ____________.
The isothermal bulk modulus of a perfect gas at pressure P is numerically equal to ____________.
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
If an average person jogs, hse produces 14.5 × 103 cal/min. This is removed by the evaporation of sweat. The amount of sweat evaporated per minute (assuming 1 kg requires 580 × 103 cal for evaparation) is ______.
Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is ______.
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
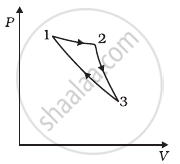
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
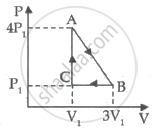
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
One mole of an ideal gas is initially kept in a cylinder with a movable frictionless and massless piston at pressure of 1.01MPa, and temperature 27°C. It is then expanded till its volume is doubled. How much work is done if the expansion is isobaric?
What is Isobaric process?
Show that the heat absorbed at constant pressure is equal to the change in enthalpy of the system.
Obtain an expression for the workdone by a gas in an isothermal process.
Write a short note on isobar.
Define isochoric process
