Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
उत्तर
(a) The passage of electric current causes heat to be generated in the resistor. The heat generated = I2Rt in standard notation.
(b) Yes. The resistor generates heat in the water.
(c) \[\ce{\underset{(Q)}{I^2Rt} = \underset{(\Delta U)}{MCΔT} + \underset{(W)}{P \Delta V}}\]
Here, I = current through the resistor, R = resistance of the resistor, t = time for which the current is passed through the resistor, M = mass of the water, S = specific heat of water, T = rise in the temperature of water, P = pressure against which the work is done by the water, Δ V = increase in the volume of the water.
(d) There is no mention of the change in volume. So, there is no work done in this case.
∴ W = 0
First law of Thermodynamics,
ΔU = Q - W
The resistor is heated due to the joules heating effect. So, that it would transfer the heat to water. So, the amount of heat Q will be negative.
ΔU = - Q - 0
ΔU = - Q
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If the system performs work at a rate of 75 Joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
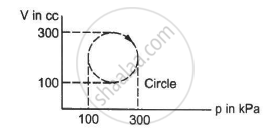
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following is an example of the first law of thermodynamics?
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
Which of the following are TRUE for a reversible isothermal process?
(i) ∆U = 0
(ii) ∆H = 0
(iii) Q = W
(iv) ∆T = 0
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample, what is the value of ΔU?
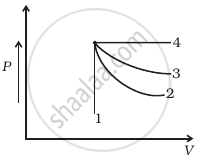
An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of 1, 2, 3 and 4 which one is adiabatic.
An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram (figure). The amount of work done by the gas is ______.

An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to final state f. Choose the correct alternatives.
- dU = 0
- dQ= 0
- dQ = dU
- dQ = dW
Can a system be heated and its temperature remains constant?
Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving. Explain.
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfect gas in a cylindrical container is shown in figure.
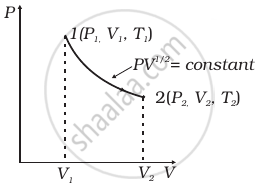
- Find the work done when the gas is taken from state 1 to state 2.
- What is the ratio of temperature T1/T2, if V2 = 2V1?
- Given the internal energy for one mole of gas at temperature T is (3/2) RT, find the heat supplied to the gas when it is taken from state 1 to 2, with V2 = 2V1.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure. Find heat exchanged by the engine, with the surroundings for each section of the cycle. (Cv = (3/2)R)
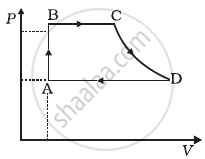
- AB : constant volume
- BC : constant pressure
- CD : adiabatic
- DA : constant pressure
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
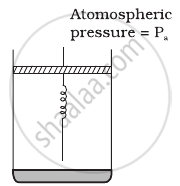
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of ______.
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
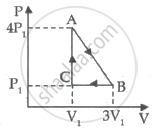
The first law of thermodynamics for isothermal process is ______.
The amount of work done in increasing the voltage across the plates of capacitor from 5 V to 10 V is W. The work done in increasing it from 10 V to 15 V will be ______.
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
104 J of work is done on a certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases 125 kJ of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas.
One mole of an ideal gas is initially kept in a cylinder with a movable frictionless and massless piston at pressure of 1.01MPa, and temperature 27°C. It is then expanded till its volume is doubled. How much work is done if the expansion is isobaric?
What is true for an adiabatic process?
Explain the formulation of first law of thrmodynamics.
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Define isochoric process
