Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A mixture of fuel and oxygen is burned in a constant-volume chamber surrounded by a water bath. It was noticed that the temperature of water is increased during the process. Treating the mixture of fuel and oxygen as the system,
- Has heat been transferred?
- Has work been done?
- What is the sign of ∆U?
उत्तर
- The heat from the chamber has been transferred to the water bath.
- The system (the mixture of fuel and oxygen) does no work because its volume does not change.
- There is an increase in the water's temperature. Therefore, ΔU is positive for water. For the system (the mixture of fuel and oxygen), ΔU is negative.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2, if brought in thermal contact, do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2)/2.
A steam engine delivers 5.4×108 J of work per minute and services 3.6 × 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the efficiency of the engine? How much heat is wasted per minute?
The outer surface of a cylinder containing a gas is rubbed vigorously by a polishing machine. The cylinder and its gas become warm. Is the energy transferred to the gas heat or work?
When we rub our hands they become warm. Have we supplied heat to the hands?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
When a tyre bursts, the air coming out is cooler than the surrounding air. Explain.
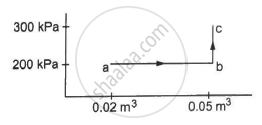
A substance is taken through the process abc as shown in figure. If the internal energy of the substance increases by 5000 J and a heat of 2625 cal is given to the system, calculate the value of J.
A gas is initially at a pressure of 100 kPa and its volume is 2.0 m3. Its pressure is kept constant and the volume is changed from 2.0 m3 to 2.5 m3. Its Volume is now kept constant and the pressure is increased from 100 kPa to 200 kPa. The gas is brought back to its initial state, the pressure varying linearly with its volume. (a) Whether the heat is supplied to or extracted from the gas in the complete cycle? (b) How much heat was supplied or extracted?
A system releases 130 kJ of heat while 109 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
Define heat.
What is the internal energy of the system, when the amount of heat Q is added to the system and the system does not do any work during the process?
When does a system lose energy to its surroundings and its internal energy decreases?
derive the relation between the change in internal energy (∆U), work is done (W), and heat (Q).
An ideal gas is compressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy will ____________.
Two samples A and B, of a gas at the same initial temperature and pressure are compressed from volume V to V/2; A isothermally and B adiabatically. The final pressure of A will be ______.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in the temperature of the gas?
In insulated systems, the amount of external work done by the gas is proportional to:
In thermodynamics, heat and work are ______.
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50 N/m2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is ______.
A steam engine delivers 4.8 x 108 Jof work per minute and services 1.2 x 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the percentage efficiency of the engine?
What is heat?
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
