Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called as?
उत्तर
Energy associated with the random, disordered motion of the molecules of a system called internal energy.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2, if brought in thermal contact, do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2)/2.
Explain why Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state A to another equilibrium state B, an amount of work equal to 22.3 J is done on the system. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, how much is the net work done by the system in the latter case? (Take 1 cal = 4.19 J)
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
A cylinder containing a gas is lifted from the first floor to the second floor. What is the amount of work done on the gas? What is the amount of work done by the gas? Is the internal energy of the gas increased? Is the temperature of the gas increased?
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
The outer surface of a cylinder containing a gas is rubbed vigorously by a polishing machine. The cylinder and its gas become warm. Is the energy transferred to the gas heat or work?
The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certain process. Is the work done by the system necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
An ideal gas is pumped into a rigid container having diathermic walls so that the temperature remains constant. In a certain time interval, the pressure in the container is doubled. Is the internal energy of the contents of the container also doubled in the interval ?
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
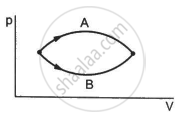
Consider the process on a system shown in figure. During the process, the work done by the system ______________ .
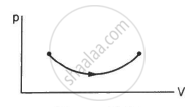
Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure.
The volumes in the initial states are the same in the two processes and the volumes in the final states are also the same. Let ∆W1 and ∆W2 be the work done by the system in the processes A and B respectively.
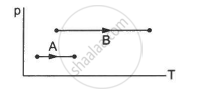
A mixture of fuel and oxygen is burned in a constant-volume chamber surrounded by a water bath. It was noticed that the temperature of water is increased during the process. Treating the mixture of fuel and oxygen as the system,
- Has heat been transferred?
- Has work been done?
- What is the sign of ∆U?
A system releases 130 kJ of heat while 109 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
Which of the following is correct, when the energy is transferred to a system from its environment?
Define heat.
Explain the different ways through which the internal energy of the system can be changed.
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam at a pressure of 1 atm. The latent heat of vaporization at this pressure is 2256 J/g. Calculate the external work and the increase in internal energy.
A cylinder containing one gram molecule of the gas was compressed adiabatically until its temperature rose from 27°C to 97°C. Calculate the work done and heat produced in the gas (𝛾 = 1.5).
When 1 g of water at 0° C and 1 x 105 N/m2 pressure is converted into ice of volume 1.082 cm3, the external work done will be ____________.
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in the temperature of the gas?
An expansion process on a diatomic ideal gas (Cv = 5/2 R), has a linear path between the initial and final coordinates on a pV diagram. The coordinates of the initial state are: the pressure is 300 kPa, the volume is 0.08 m3 and the temperature is 390 K. The final pressure is 90 kPa and the final temperature s 320 K. The change in the internal energy of the gas, in SI units, is closest to:
The molar specific heat of He at constant volume is 12.47 J/mol.K. Two moles of He are heated at constant pressure. So the rise in temperature is 10 K. Find the increase in internal energy of the gas.
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
