Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics for the Isobaric process.
उत्तर
Usually, chemical reactions are carried out in open containers under constant atmospheric pressure. In such reactions, ∆V ≠ 0
∵ ∆U = Q - Pext ∆V ...(1)
Replacing Q by Qp and ∆U by Qp - Pext ∆V in equation (1) gives
Qp = ∆U + Pext ∆V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If the system performs work at a rate of 75 Joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
A system can be taken from the initial state p1, V1 to the final state p2, V2 by two different methods. Let ∆Q and ∆W represent the heat given to the system and the work done by the system. Which of the following must be the same in both the methods?
The internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system.
(a) The process must be adiabatic.
b) The process must be isothermal.
(c) The process must be isobaric.
(d) The temperature must decrease.
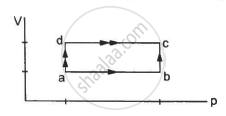
When a system is taken through the process abc shown in figure, 80 J of heat is absorbed by the system and 30 J of work is done by it. If the system does 10 J of work during the process adc, how much heat flows into it during the process?
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

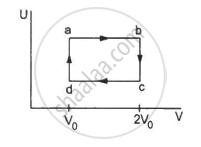
Figure shows the variation in the internal energy U with the volume V of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas in a cyclic process abcda. The temperatures of the gas at b and c are 500 K and 300 K respectively. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas during the process.
A resistor held in running water carries electric current. Treat the resistor as the system
- Does heat flow into the resistor?
- Is there a flow of heat into the water?
- Is any work done?
- Assuming the state of resistance to remain unchanged, apply the first law of thermodynamics to this process.
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly at 300 K from 1 L to 10 L. The enthalpy change in kJ is ______.
Based on first law of thermodynamics which of the following is correct.
For a particular reaction, the system absorbs 8 kJ of heat and does 2.5 kJ of work on its surrounding. What will be the change in internal energy of the system?
Calculate the amount of work done during isothermal expansion of a gas from a volume of 4 dm3 to 6 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3 atmosphere?
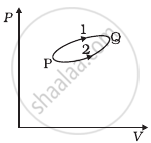
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
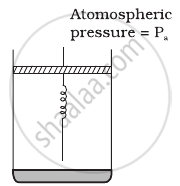
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of ______.
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
One mole of an ideal gas is allowed to expand reversibly and adiabatically from a temperature of 27°C. If the work done during the process is 3 kJ, the final temperature will be equal to ______.
(Cv = 20 JK−1)
If one mole of monoatomic gas `(gamma=5/3)` is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas `(gamma=7/5)`, the value of γ for the mixture is ______.
ΔU = 0 is true for ______.
An ideal gas having pressure p, volume V and temperature T undergoes a thermodynamic process in which dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then, for the gas ______.
In an adiabatic process, ______.
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
What is Isobaric process?
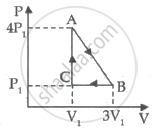
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Show that the heat absorbed at constant pressure is equal to the change in enthalpy of the system.
