Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the mathematical equation for the first law of thermodynamics for:
Isothermal process
Deduce the first law of thermodynamics for the isothermal process.
उत्तर
For isothermal process:
For a given temperature (T) and internal energy (U) of the remains constant.
∴ ΔT = 0
∴ ΔU = 0
First law of thermodynamic
ΔU = Q + W
0 = Q + W ...(∵ ΔU = 0)
∴ Q = – W
संबंधित प्रश्न
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
50 cal of heat should be supplied to take a system from the state A to the state B through the path ACB as shown in figure. Find the quantity of heat to be suppled to take it from A to B via ADB.

Answer the following in one or two sentences.
State the first law of thermodynamics.
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
Define an isolated system.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
Consider two containers A and B containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container A is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container B is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in B to that of gas in A is ______.
Consider a cycle followed by an engine (Figure)
1 to 2 is isothermal
2 to 3 is adiabatic
3 to 1 is adiabatic
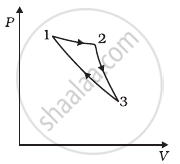
Such a process does not exist because ______.
- heat is completely converted to mechanical energy in such a process, which is not possible.
- mechanical energy is completely converted to heat in this process, which is not possible.
- curves representing two adiabatic processes don’t intersect.
- curves representing an adiabatic process and an isothermal process don’t intersect.
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
Consider one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder of unit cross section with a piston attached (figure). A spring (spring constant k) is attached (unstretched length L) to the piston and to the bottom of the cylinder. Initially the spring is unstretched and the gas is in equilibrium. A certain amount of heat Q is supplied to the gas causing an increase of volume from V0 to V1.
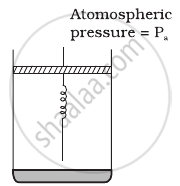
- What is the initial pressure of the system?
- What is the final pressure of the system?
- Using the first law of thermodynamics, write down a relation between Q, Pa, V, Vo and k.
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 4 moles of a rigid diatomic gas from 0°C to 50°C when no work is done is ______.
(R is the universal gas constant.)
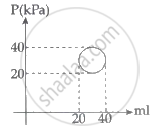
In the reported figure, heat energy absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process is ______ πJ.
200g water is heated from 40°C to 60°C. Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to ______.
(Given specific heat of water = 4184 J/kgK)
An insulated container of gas has two chambers separated by an insulating partition. One of the chambers has volume V1 and contains ideal gas at pressure P1 and temperature T1. The other chamber has volume V2 and contains ideal gas at pressure P2 and temperature T2. If the partition is removed without doing any work on the gas, the final equilibrium temperature of the gas in the container will be ______.
A soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 3 cm and another soap bubble in vacuum has a radius of 4 cm. If the two bubbles coalesce under isothermal condition, then the radius of the new bubble is ______.
The amount of work done in increasing the voltage across the plates of capacitor from 5 V to 10 V is W. The work done in increasing it from 10 V to 15 V will be ______.
The V cc volume of gas having `γ = 5/2` is suddenly compressed to `(V/4)` cc. The initial pressure of the gas is p. The final pressure of the gas will be ______.
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
Derive an expression for the work done during an isothermal process.
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
In an adiabatic expansion of 2 moles of a gas, the initial pressure was 1.013 × 105 Pa, the initial volume was 22.4 L, the final pressure was 3.191 × 104 Pa and the final volume was 44.8 L. Find the work done by the gas on its surroundings. Taken `γ = 5/3`.
What is Isobaric process?
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Obtain an expression for the workdone by a gas in an isothermal process.
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
Define isochoric process
What is an isothermal process?
