Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
उत्तर
(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
The process that takes place through A and returns back to the same state through B is cyclic. Being a state function, net change in internal energy, ∆U will be zero, i.e.
∆U1 (Change in internal energy in process A) = ∆U2 (Change in internal energy in process B)
\[\Rightarrow \Delta U = \Delta U_1 + \Delta U_2 = 0\]
Here, ∆U is the total change in internal energy in the cyclic process.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, we get
\[\Delta Q - \Delta W = \Delta U\]
Here, ∆Q is the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W is the net work done by the system in the process A + B.
Thus,
∆Q - ∆W = 0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The internal energy of a gas is given by U = 1.5 pV. It expands from 100 cm3 to 200 cm3against a constant pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas in the process.
Calculate the increase in the internal energy of 10 g of water when it is heated from 0°C to 100°C and converted into steam at 100 kPa. The density of steam = 0.6 kg m−3. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and the latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.25 × 10 6J kg−1.
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is enclosed in a rigid insulating cylinder. It is ignited by a spark. The temperature and pressure both increase considerably. Assume that the energy supplied by the spark is negligible, what conclusions may be drawn by application of the first law of thermodynamics?
ΔU is equal to ____________ work.
A gas performs 0.320 kJ work on surrounding and absorbs 120 J of heat from the surrounding. Hence, change in internal energy is ______.
The isothermal bulk modulus of a perfect gas at pressure P is numerically equal to ____________.
Change in internal energy, when 4 KJ of work is done on the system and 1 KJ heat is given out by the system, is:
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
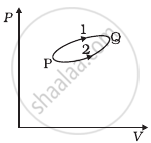
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
Is it possible to increase the temperature of a gas without adding heat to it? Explain.
The initial state of a certain gas is (Pi, Vi, Ti). It undergoes expansion till its volume becomes Vf. Consider the following two cases:
- the expansion takes place at constant temperature.
- the expansion takes place at constant pressure.
Plot the P-V diagram for each case. In which of the two cases, is the work done by the gas more?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
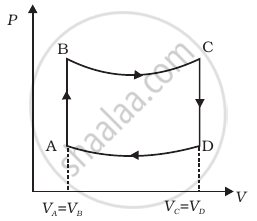
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
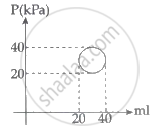
In the reported figure, heat energy absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process is ______ πJ.
200g water is heated from 40°C to 60°C. Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to ______.
(Given specific heat of water = 4184 J/kgK)
The V cc volume of gas having `γ = 5/2` is suddenly compressed to `(V/4)` cc. The initial pressure of the gas is p. The final pressure of the gas will be ______.
An ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is expanded adiabatically. How many times has the gas had to be expanded to reduce the root mean square velocity of molecules two times?
Consider the cyclic process ABCA on a sample of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas as shown in following figure. The temperature of the gas at A and B are 300 K and 500 K respectively. A total of 1200 J heat is withdrawn from the sample in this process. Find the work done by the gas in part BC. (R = 8.3 J/mol K)
Choose the correct relation with reason.
Write a short note on isobar.
Define the isothermal process.
