Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three copper blocks of masses M1, M2 and M3 kg respectively are brought into thermal contact till they reach equilibrium. Before contact, they were at T1, T2, T3 (T1 > T2 > T3). Assuming there is no heat loss to the surroundings, the equilibrium temprature T is (s is specific heat of copper)
पर्याय
`T = (T_1 + T_2 + T_3)/3`
`T = (M_1T_1 + M_2T_2 + M_3T_3)/(M_1 + M_2 + M_3)`
`T = (M_1T_1 + M_2T_2 + M_3T_3)/(3(M_1 + M_2 + M_3))`
`T = (M_1T_1s + M_2T_2s + M_3T_3s)/(M_1 + M_2 + M_3)`
उत्तर
`T = (M_1T_1 + M_2T_2 + M_3T_3)/(M_1 + M_2 + M_3)`
Explanation:
Let the equilibrium temperature to be found be T. Now, we consider T to be greater than T1 and T2 but smaller than T3.
Since there is no loss of heat energy. Hence, we get,
Heat lost by M3 = Heat regained by M1 + Heat regained by M2 So, we get,
⇒ M3s (T3 – T) = M1s (T – T1) + M2s (T – T2)
Dividing both sides by s, we get,
⇒ M3 (T3 – T) = M1 (T – T1) + M2 (T – T2)
Opening the brackets and solving for T, we get,
⇒ M3T3 – M3T = M1T – M1T1 + M2T – M2T2
⇒ M3T3 + M1T1 + M2T2 = M1T + M2T + M3T
⇒ `T = (M_1T_1 + M_2T_2 + M_3T_3)/(M_1 + M_2 + M_3)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of ____________ .
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
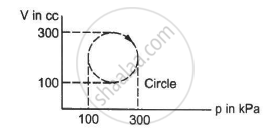
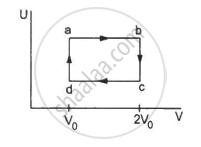
Figure shows the variation in the internal energy U with the volume V of 2.0 mol of an ideal gas in a cyclic process abcda. The temperatures of the gas at b and c are 500 K and 300 K respectively. Calculate the heat absorbed by the gas during the process.
The process, in which no heat enters or leaves the system, is termed as ____________.
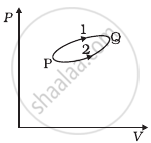
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
Consider a cycle tyre being filled with air by a pump. Let V be the volume of the tyre (fixed) and at each stroke of the pump ∆V(V) of air is transferred to the tube adiabatically. What is the work done when the pressure in the tube is increased from P1 to P2?
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
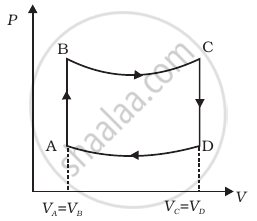
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
An ideal gas is taken through series of changes ABCA. The amount of work involved in the cycle is ______.
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
Using the first law of thermodynamics, show that for an ideal gas, the difference between the molar specific heat capacities at constant pressure and at constant volume is equal to the molar gas constant R.
